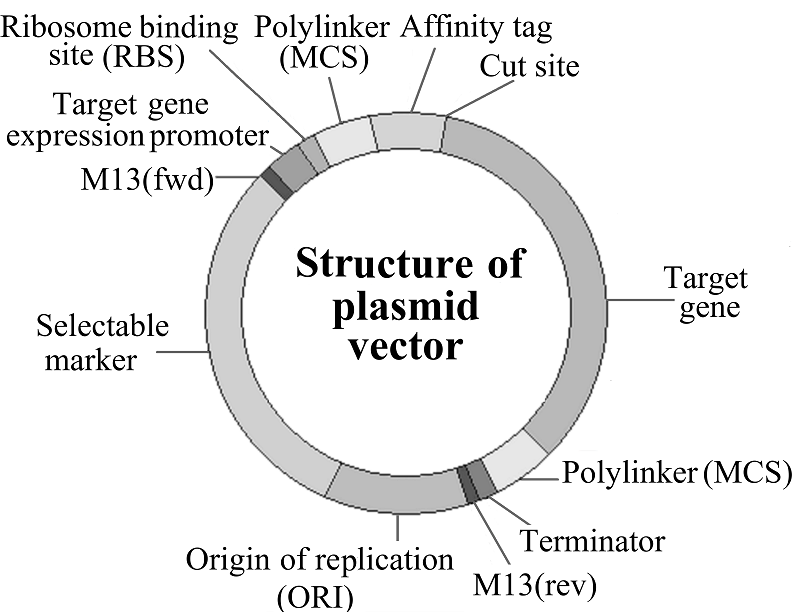
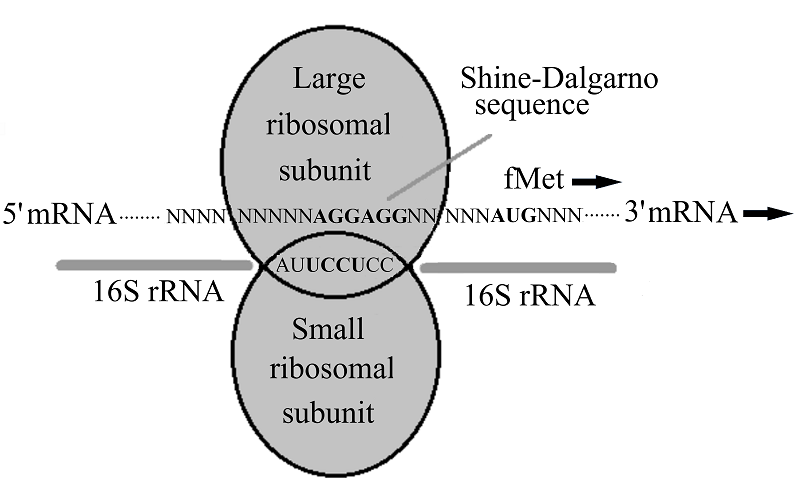
HETEROLOGOUS EXPRESSION OF RECOMBINANT L-ASPARAGINASE GENES
(Dedicated to late Professor N.N. Sokolov, who made a significant contribution in the field of L-asparaginase)
Institute of Biomedical Chemistry, 10 Pogodinskaya str., Moscow, 119121; *e-mail: Ivan1190@yandex.ru
Keywords:L-asparaginase, expression optimization, heterologous expression, rational and computer-aided design, recombinant genes
DOI:10.18097/BMCRM00265
L-asparaginase (EC 3.5.1.1.) is the enzyme with the highest level of global production and is used in the treatment of cancer and in the food industry. Different expression systems are used for the production of many target proteins, ranging from cell-free to hyperproductive plant, insect, bacterial and mammalian cells. This review attempts to bring together the available literature data on heterologous gene expression and technology for the production of recombinant L-asparaginases.
FUNDING
The work was carried out within the framework of the Program of Fundamental Scientific Research in the Russian Federation for the long-term period (2021-2030) (No. 122022800499-5).
REFERENCES
- Loch, J., Jaskolski, M. (2021) Structural and biophysical aspects of L-asparaginases: A growing family with amazing diversity. IUCrJ, 8 (4), 514-531. DOI
- Brumano, L., da Silva, F.V.S., Costa-Silva, T., Apolinário, A., Santos, J., Kleingesinds, E., Monteiro, G., Rangel-Yagui, C., Benyahia, B., Junior, A. (2019) Development of L-asparaginase biobetters: current research status and review of the desirable quality profiles. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology, 10(6), 212. DOI
- Cachumba, J.J., Antunes, F.A., Peres, G.F., Brumano, L.P., Santos, J.C., Da Silva, S.S. (2016) Current applications and different approaches for microbial L-asparaginase production. Brazilian journal of microbiology : [publication of the Brazilian Society for Microbiology], 47 (Suppl 1), 77-85. DOI
- Eisele, N., Linke, D., Bitzer, K., Na’amnieh, S., Nimtz, M., Berger, R. (2011) The first characterized asparaginase from a basidiomycete, Flammulina velutipes. Bioresource technology, 102(3), 3316-3321. DOI
- Jha, S. K., Pasrija, D., Sinha, R., Singh, H.R., Nigam, V., Vidyarthi, A. (2012) Microbial L-asparaginase: a review on current scenario and future prospects. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 3(9), 3076- 3090. DOI
- Dumina, M., Zhgun, A., Pokrovskaya, M., Aleksandrova, S., Zhdanov, D., Sokolov, N., El’darov, M. (2021) Highly active thermophilic L-asparaginase from Melioribacter roseus represents a novel large group of type II bacterial L-asparaginases from chlorobi-ignavibacteriae-bacteroidetes clade. International journal of molecular sciences, 22(24), 13632. DOI
- Mahajan, R.V., Kumar, V., Rajendran, V., Saran, S., Ghosh, P.C., Saxena, R.K. (2014) Purification and characterization of a novel and robust L-asparaginase having low-glutaminase activity from Bacillus licheniformis: in vitro evaluation of anti-cancerous properties. PLoS One, 9(6):e99037. DOI
- Sarquis, M.I., Oliveira, E.M., Santos, A.S., Costa, G.L. (2004) Production of L-asparaginase by filamentous fungi. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz. 99(5), 489-492. DOI
- da Cunha, M.C, Dos Santos, Aguilar, J.G., de Melo, R.R., Nagamatsu, S.T., Ali, F., de Castro, R.J.S., Sato, H.H. (2019) Fungal L-asparaginase: Strategies for production and food applications. Food research international, 126, 108658. DOI
- Saleh, A.A., El-Aref, H.M., Ezzeldin, A.M., Ewida R.M., Bedak, O.A.Al. (2025) L-asparaginase from the novel Fusarium falciforme AUMC 16563: extraction, purification, characterization, and cytotoxic effects on PC-3, HePG- 2, HCT-116, and MCF-7 cell lines. BMC microbiology, 25(1), 145. DOI
- Casado, A., Caballero, J.L., Franco, A.R., Cárdenas, J., Grant, M.R., Muñoz-Blanco, J. (1995) Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the L-asparaginase gene of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant physiology, 108(3), 1321- 1322. DOI
- Sharma, A., Kaushik., V., Goel, M. (2022) Insights into the distribution and functional properties of L-asparaginase in the Archaeal domain and characterization of Picrophilus torridus asparaginase belonging to the novel family Asp2like1. ACS Omega, 7(45), 40750-40765. DOI
- Broome, J.D. (1965) Antilymphoma activity of L-asparaginase in vivo: clearance rates of enzyme preparations from guinea pig serum and yeast in relation to their effect on tumor growth. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 35(6), 967-974. DOI
- Lopes, A.M., Oliveira-Nascimento, L., Ribeiro, A., Tairum, C.A. Jr., Breyer, C.A., Oliveira, M.A., Monteiro, G., Souza-Motta, C.M., Magalhães, P.O., Avendaño, J.G., Cavaco-Paulo, A.M., Mazzola, P.G., Rangel-Yagui, C.O., Sette, L.D., Converti, A., Pessoa, A. (2017) Therapeutic L-asparaginase: upstream, downstream and beyond. Critical reviews in biotechnology, 37(1), 82-99. DOI
- Bosmann, H.B., Kessel, D. (1970) Inhibition of glycoprotein synthesis in L5178Y mouse leukaemic cells by L-asparaginase in vitro. Nature. 226(5248), 850-851. DOI
- Bejger, M., Imiolczyk, B., Clavel, D., Gilski, M., Pajak, A., Marsolais, F., Jaskolski, M. (2014) Na⁺/K⁺ exchange switches the catalytic apparatus of potassium-dependent plant L-asparaginase. Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography, 70(Pt 7),1854-1872. DOI
- Vimal, A., Kumar, A. (2020) Antimicrobial potency evaluation of free and immobilized L-asparaginase using chitosan nanoparticles. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 61(6), 102231. DOI
- Vimal, A., Kumar, A. (2022) L-asparaginase: Need for an expedition from an enzymatic molecule to antimicrobial drug. International journal of peptide research and therapeutics. 28(1), 9. DOI
- Zielezinski, A., Loch, J.I., Karlowski, W.M., Jaskolski, M. (2022) Massive annotation of bacterial L-asparaginases reveals their puzzling distribution and frequent gene transfer events. Scientific reports.12(1),15797. DOI
- Abd El-Baky, H.H., El-Baroty, G.S. (2020) Spirulina maxima L-asparaginase: immobilization, antiviral and antiproliferation activities. Recent patents on biotechnology, 14(2), 154-163. DOI
- Vimal, A., Kumar, A. (2018) L-Asparaginase: a feasible therapeutic molecule for multiple diseases. 3 Biotech, 8(6), 278. DOI
- Darvishi, F., Jahanafrooz, Z., Mokhtarzadeh, A. (2022) Microbial L-asparaginase as a promising enzyme for treatment of various cancers. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 106(17), 5335-5347. DOI
- Ściuk, A., Wątor, K., Staroń, I., Worsztynowicz, P., Pokrywka, K., Sliwiak, J., Kilichowska, M., Pietruszewska, K., Mazurek, Z., Skalniak, A., Lewandowski, K., Jaskolski, M., Loch, J.I., Surmiak, M. (2024). Substrate affinity is not crucial for therapeutic L-asparaginases: antileukemic activity of novel bacterial enzymes. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 29(10), 2272. DOI
- Wang, N., Ji, W., Wang, L., Wu, W., Zhang, W., Wu, Q., Du, W., Bai, H., Peng, B., Ma, B., Li, L. (2022) Overview of the structure, side effects, and activity assays of L-asparaginase as a therapy drug of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. RSC medicinal chemistry, 13(2), 117-128. DOI
- Patel, P., Panseriya, H., Vala, A.K., Dave, B.P., Gosai, H. (2022). Exploring current scenario and developments in the field of microbial L-asparaginase production and applications: A review. Process Biochemistry, 121, 529-541. DOI
- Xu, F., Oruna-Concha, M.J., Elmore, J.S. (2016) The use of asparaginase to reduce acrylamide levels in cooked food. Food chemistry. 210, 163-171. DOI
- Santos, J.H.P.M., Costa, I.M., Molino, J.V.D., Leite, M.S.M., Pimenta, M.V., Coutinho, J.A.P., Pessoa, A.Jr., Ventura, S.P.M., Lopes, A.M., Monteiro, G. (2017) Heterologous expression and purification of active L-asparaginase I of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in E. coli host. Biotechnology progress, 33(2), 416- 424. DOI
- Tekoah, Y., Shulman, A., Kizhner, T., Ruderfer, I., Fux, L., Nataf, Y., Bartfeld, D., Ariel, T., Gingis-Velitski, S., Hanania, U., Shaaltiel, Y. (2015) Largescale production of pharmaceutical proteins in plant cell culture-the Protalix experience. Plant biotechnology journal. 13(8), 1199-1208. DOI
- Zhu, J. (2012) Mammalian cell protein expression for biopharmaceutical production. Biotechnology advances, 30(5), 1158-1170. DOI
- Zhang, X. Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Li, X., Zhu, M., Zhang, H., Xu, M., Yang, T., Rao, Z. (2021) Heterologous expression and rational design of L-asparaginase from Rhizomucor miehei to improve thermostability. Biology, 10(12), 1346. DOI
- Lefin, N., Miranda, J., Beltrán, J.F., Belén, L.H., Effer, B., Pessoa, A. Jr., Farias, J.G., Zamorano, M. (2023) Current state of molecular and metabolic strategies for the improvement of L-asparaginase expression in heterologous systems. Frontiers in pharmacology, 14, 1208277. DOI
- Yang, X., Rao, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, J., Liu, W., Cai, D., Chen, S. (2023) Efficient production of L-asparaginase in Bacillus licheniformis by optimizing expression elements and host. Chinese journal of biotechnology, 39(3), 1096- 1106. DOI
- Li, X., Xu, S., Zhang, X., Xu, M., Yang, T., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Fang, H., Osire, T., Yang, S., Rao, Z. ( 2019) Design of a high-efficiency synthetic system for L-asparaginase production in Bacillus subtilis. Engineering in life sciences, 19(3), 229-239. DOI
- Costa-Silva, T.A., Camacho-Córdova, D.I., Agamez-Montalvo, G.S., Parizotto, L.A., Sánchez-Moguel, I., Pessoa-Jr, A. (2019) Optimization of culture conditions and bench-scale production of anticancer enzyme L-asparaginase by submerged fermentation from Aspergillus terreus CCT 7693. Preparative biochemistry & biotechnology, 49(1), 95-104. DOI
- Sharma, D., Mishra, A. (2023) Synergistic effects of ternary mixture formulation and process parameters optimization in a sequential approach for enhanced L-asparaginase production using agro-industrial wastes. Environmental science and pollution research international, 31(12), 1-16. DOI
- Poluri, K.M., Gulati, K. (2017) Rational designing of novel proteins through computational approaches. In: Protein engineering techniques.Springer Briefs in Applied Sciences and Technology. Springer Singapore. pp. 61-83. DOI
- Praveen, P. (2019). Modeling and validation of L-asparaginase enzyme, an anticancer agent using the tools of computational biology. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 8(1), 211-214, DOI
- Kelley, L.A., Mezulis, S., Yates, C.M., Wass, M.N., Sternberg, M.J. (2015) The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nature protocols, 10(6), 845-858. DOI
- Gileadi, O. (2017) Recombinant protein expression in E. coli : A historical perspective. Methods in molecular biology, 1586, 3-10. DOI
- Saberianfar, R., Menassa, R. (2018) Strategies to increase expression and accumulation of recombinant proteins. In: Molecular Pharming: Applications, Challenges, and Emerging Areas. ( A.R. Kermode and L. Jiang eds.) New York. pp. 119-135. DOI
- Shishparenok, A.N., Gladilina, Y.A., Zhdanov, D.D. (2023) Engineering and expression strategies for optimization of L-asparaginase development and production. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(20),15220. DOI
- Miranda, J., Lefin, N., Beltran, J., Belén, L.H., Tsipa, A., Farias, J.G., Zamorano, M. (2023) Enzyme engineering strategies for the bioenhancement of L-asparaginase used as a biopharmaceutical. BioDrugs : clinical immunotherapeutics, biopharmaceuticals and gene therapy, 37(6), 793-811. DOI
- Borek, D., Jaskólski, M. (2001) Sequence analysis of enzymes with asparaginase activity. Acta biochimica Polonica, 48(4), 893-902. DOI
- Michalska, K., Jaskolski, M. (2006). Structural aspects of L-asparaginases, their friends and relations. Acta biochimica Polonica, 53 (4), 627-640. DOI
- Castro, D., Marques, A., Almeida, M.R., de Paiva, G.B., Bento, H.B.S., Pedrolli, D.B., Freire, M.G., Tavares, A.P.M., Santos-Ebinuma, V.C. (2021) L-asparaginase production review: bioprocess design and biochemical characteristics. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 105(11), 4515-4534. DOI
- Bonthron, D.T., Jaskólski, M. (1997) Why a “benign” mutation kills enzyme activity. Structure-based analysis of the A176V mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae L-asparaginase I. Acta biochimica Polonica, 44(3), 491-504. DOI
- Lubkowski, J., Wlodawer, A. (2021) Structural and biochemical properties of L-asparaginase. The FEBS journal, 288(14), 4183-4209. DOI
- da Silva, L.S., Doonan, L.B., Pessoa, A. Jr., de Oliveira, M.A., Long, P.F. (2022) Structural and functional diversity of asparaginases: Overview and recommendations for a revised nomenclature. Biotechnology and applied biochemistry, 69(2), 503-513. DOI
- Yun, M.K., Nourse, A., White, S.W., Rock, C.O., Heath, R.J. (2007) Crystal structure and allosteric regulation of the cytoplasmic E. coli L-asparaginase I. Journal of molecular biology, 369(3), 794-811. DOI
- Jennings, M.P., Beacham, I.R. (1993) Co-dependent positive regulation of the ansB promoter of E. coli by CRP and the FNR protein: a molecular analysis. Molecular microbiology, 9(1), 155-64. DOI
- Dunlop, P.C., Meyer, G.M., Ban, D., Roon, R.J. (1978) Characterization of two forms of asparaginase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Journal of biological chemistry, 253(4), 1297-1304. DOI
- Dumina, M., Zhgun, A. (2023) Thermo-L-asparaginases: from the role in the viability of thermophiles and hyperthermophiles at high temperatures to a molecular understanding of their thermoactivity and thermostability. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(3), 2674. DOI
- Pokrovskaya, M.V., Pokrovsky, V.S., Aleksandrova, S.S., Sokolov, N.N., Zhdanov, D.D. (2022) Molecular analysis of L-asparaginases for clarification of the mechanism of action and optimization of pharmacological functions. Pharmaceutics, 14(3), 599. DOI
- Kotzia, G.A., Lappa, K., Labrou, N.E. ( 2007) Tailoring structure-function properties of L-asparaginase: engineering resistance to trypsin cleavage. The Biochemical journal, 404(2), 337-343. DOI
- Gesto, D.S., Cerqueira, N.M., Fernandes, P.A., Ramos, M.J. (2013) Unraveling the Enigmatic Mechanism of L-asparaginase II with Q M/QM Calculations. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135(19), 7146-7158. DOI
- Aghaiypour, K., Wlodawer, A., Lubkowski, J. (2001) Structural basis for the activity and substrate specificity of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase. Biochemistry, 40(19), 5655-5664. DOI
- Upadhyay, A.K., Singh, A., Mukherjee, K.J., Panda, A.K. (2014) Refolding and purification of recombinant L-asparaginase from inclusion bodies of E. coli into active tetrameric protein. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 486. DOI
- Maurizi, M.R. (1992) Proteases and protein degradation in Escherichia coli. Experientia, 48(2), 178-201. DOI
- Wülfing, C., Plückthun, A. (1994) Protein folding in the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Molecular microbiology, 12(5), 685-692. DOI
- Papageorgiou, A.C., Posypanova, G.A., Andersson, C.S., Sokolov, N.N., Krasotkina, J. (2008) Structural and functional insights into Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase. The FEBS journal, 275(17), 4306-4316. DOI
- Swain, A.L., Jaskólski, M., Housset, D., Rao, J.K., Wlodawer, A. (1993) Crystal structure of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase, an enzyme used in cancer therapy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90(4), 1474-1478. DOI
- Pokrovskaya, M.V., Pokrovskiy, V.S., Aleksandrova, S.S, Anisimova, N.Iu., Andrianov, R.M., Treschalina, E.M., Ponomarev, G.V., Sokolov, N.N. (2013). Recombinant intracellular Rhodospirillum rubrum L-asparaginase with low L-glutaminase activity and antiproliferative effect. Biomeditsinskaia Khimiia, 59(2), 192-208. DOI
- Palm, G.J., Lubkowski, J., Derst, C., Schleper, S., Röhm, K.H., Wlodawer, A. (1996) A covalently bound catalytic intermediate in Escherichia coli asparaginase: crystal structure of a Thr-89-Val mutant. FEBS letters, 390(2), 211-216. DOI
- El-Ghonemy, D. (2014) Microbial amidases and their industrial applications: A review. Journal of Medical Microbiology and Diagnosis, 4, 1-6. DOI
- Borek, D., Kozak, M., Pei, J., Jaskolski, M. (2014) Crystal structure of active site mutant of antileukemic L-asparaginase reveals conserved zinc-binding site. The FEBS journal, 81(18), 4097-4111. DOI
- Nguyen, H.A., Su, Y., Lavie, A. (2016) Design and characterization of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase variants with diminished L-glutaminase activity. The Journal of biological chemistry, 291(34), 17664-17676. DOI
- Nguyen, H.A, Su, Y., Lavie, A. (2016) Structural insight into substrate selectivity of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase. Biochemistry, 55(8), 1246- 1253. DOI
- Nguyen, H.A., Durden, D.L., Lavie, A. (2017) The differential ability of asparagine and glutamine in promoting the closed/active enzyme conformation rationalizes the Wolinella succinogenes L-asparaginase substrate specificity. Scientific reports, 7, 41643. DOI
- Lubkowski, J., Wlodawer, A. (2019) Geometric considerations support the double-displacement catalytic mechanism of L-asparaginase. Protein science: a publication of the Protein Society, 28(10), 1850-1864. DOI
- Lubkowski, J., Vanegas, J.M., Chan, W.K., Lorenzi, P., Weinstein, J., Sukharev, S., Fushman, D., Rempe, S., Anishkin, A., Wlodawer, A. (2020) Mechanism of catalysis by L-asparaginase. Biochemistry, 59(20), 1927-1945. DOI
- Min Yao, Yoshiaki Yasutake, Hazuki Morita, Isao Tanaka. Structure of the type I L-asparaginase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii at 2.16 A resolution Acta Crystallographica Section D: Structural Biology (2005) 61(Pt 3):294-301. DOI
- Tomar, R., Garg, D.K., Mishra, R., Thakur, A.K., Kundu, B. (2013) N-terminal domain of Pyrococcus furiosus L-asparaginase functions as a nonspecific, stable, molecular chaperone. The FEBS journal, 280(11), 2688-2699. DOI
- Pritsa, A.A., Kyriakidis, D.A. (2001) L-asparaginase of Thermus thermophilus: Purification, properties and identification of essential amino acids for its catalytic activity. Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 216 (1-2), 93-101. DOI
- Derst, C., Henseling, J., Röhm, K.H. (1992) Probing the role of threonine and serine residues of E. coli asparaginase II by site-specific mutagenesis. Protein engineering, 5(8), 785-789. DOI
- Derst, C., Henseling, J., Röhm, K.H. (2000) Engineering the substrate specificity of Escherichia coli asparaginase. II. Selective reduction of glutaminase activity by amino acid replacements at position 248. Protein science: a publication of the Protein Society, 9(10), 2009-2017. DOI
- Derst, C., Wehner, A., Specht, V., Röhm, K.H. (1994) States and functions of tyrosine residues in Escherichia coli asparaginase II. European journal of biochemistry, 224(2), 533-540. DOI
- Bansal, S., Srivastava, A., Mukherjee, G., Pandey, R., Verma, A.,K. Mishra, P., Kundu, B. (2012) Hyperthermophilic asparaginase mutants with enhanced substrate affinity and antineoplastic activity: structural insights on their mechanism of action. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 26(3), 1161-1171. DOI
- Offman, M.N., Krol, M., Patel, N., Krishnan, S., Liu, J., Saha, V., Bates, P.A. (2011) Rational engineering of L-asparaginase reveals importance of dual activity for cancer cell toxicity. Blood. 117(5), 1614-1621. DOI
- Costa, I.M., Schultz, L., de Araujo Bianchi, P.B., Leite, M.S., Farsky, S.H., de Oliveira, M.A., Pessoa, A., Monteiro, G. (2016) Recombinant L-asparaginase ׀ from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: an allosteric enzyme with antineoplastic activity. Scientific reports, 6(1), 36239. DOI
- Karamitros, C.S., Konrad, M. (2014) Bacterial co-expression of the α and β protomers of human L-asparaginase-3: Achieving essential N-terminal exposure of a catalytically critical threonine located in the β-subunit. Protein expression and purification, 93, 1-10. DOI
- Karamitros, C.S., Konrad, M. (2014) Human 60-kDa lysophospholipase contains an N-terminal L-asparaginase domain that is allosterically regulated by L-asparagine. The Journal of biological chemistry, 289(19), 12962-12975. DOI
- Maqsood, B., Basit. A., Khurshid, M., Bashir, Q. (2020) Characterization of a thermostable, allosteric L-asparaginase from Anoxybacillus flavithermus. International journal of biological macromolecules, 152, 584-592. DOI
- Mihooliya, K.N., Nitika, N., Bhambure, R., Rathore, A. (2022) Post-refolding stability considerations for optimization of in-vitro refolding: L-asparaginase as a case study. Biotechnology journal, 18(4), 2200505. DOI
- Schymkowitz, J., Borg, J., Stricher, F., Nys, R., Rousseau, F., Serrano, L. (2005) The FoldX web server: an online force field. Nucleic acids research, 33(Web Server issue):W382-8. DOI
- Dastmalchi, M., Alizadeh, M., Jamshidi-Kandjan, O., Rezazadeh, H., Hamzeh-Mivehroud, M., Farajollahi, M.M., Dastmalchi, S. (2023) Expression and biological evaluation of an engineered recombinant L-asparaginase designed by In Silico method based on sequence of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Advanced pharmaceutical bulletin, 13(4), 827-836. DOI
- Goyal, G., Bhatt, V.R. (2015) L-asparaginase and venous thromboembolism in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Future oncology (London, England), 11(17), 2459-2470. DOI
- Schmiegelow, K., Attarbaschi, A., Barzilai, S., Escherich, G., Frandsen, T., Halsey, C.,Hough, R., Jeha, S., Kato, M., Liang, D.C., Mikkelsen, T.S., Möricke, A., Niinimäki, R., Piette, C., Putti, M.C., Raetz, E., Silverman, L.B., Skinner, R., Tuckuviene, R., van der Sluis, I., Zapotocka, E. (2016) Consensus definitions of 14 severe acute toxic effects for childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia treatment: A delphi consensus. The Lancet. Oncology, 17 (6), e231–e239. DOI
- Zhang, Z.X., Nong, F.T., Wang, Y.Z, Yan, C.-X., Gu, Y., Song, P., Sun, X.M. (2022) Strategies for efficient production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli: alleviating the host burden and enhancing protein activity. Microbial Cell Factories, 21(1), 191. DOI
- Zhang, S., Sun, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, F., Gao, W. (2023) Thermoresponsive polypeptide fused L-asparaginase with mitigated immunogenicity and enhanced efficacy in treating hematologic malignancies. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), 10(23):e2300469. DOI
- Zhang, W., Dai, Q., Huang, Z., Xu, W. (2023) Identiication and thermostability modification of the mesophilic L-asparaginase from Limosilactobacillus secaliphilus. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 196(6), 1-15. DOI
- Kishore, V., Nishita, K.P., Manonmani, H.K. (2015) Cloning, expression and characterization of L-asparaginase from Pseudomonas fluorescens for large scale production in E. coli BL21. 3 Biotech. 5(6), 975-981. DOI
- Wang, Y., Xu, W., Wu, H., Zhang, W., Guang, C., Mu, W. (2021) Microbial production, molecular modification, and practical application of L-Asparaginase: A review. International journal of biological macromolecules, 186, 975-983. DOI
- Pokrovskaya, M.V., Aleksandrova, S.S., Pokrovsky, V.S., Omeljanjuk, N.M., Borisova A.A., Anisimova, N.Y., Sokolov, N.N. (2012) Cloning, expression and characterization of the recombinant Yersinia pseudotuberculosis L-asparaginase. Protein expression and purification, 82(1), 150-154. DOI
- Maggi, M., Mittelman, S.D., Parmentier, J.H., Colombo, G., Meli, M., Whitmire, J.M., Merrell, D.S., Whitelegge, J., Scotti, C. (2017) A proteaseresistant Escherichia coli asparaginase with outstanding stability and enhanced anti-leukaemic activity in vitro. Scientific reports, 7(1), 14479. DOI
- Mahboobi, M., Salmanian, A.H., Sedighian, H., Bambai, B. (2023) Molecular modeling and optimization of type II E.coli L-asparginase activity by in silico design and in vitro site-directed mutagenesis. The protein journal, 42(6), 664-674. DOI
- Mahboobi, M., Sedighian, H., Hedayati, M., Bambai, B., Saeed, E., Soofian, A.J. (2017) Applying bioinformatic tools for modeling and modifying type II E.coli L-asparginase to present a better therapeutic agent/drug for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. International Journal of Cancer Management, 10(3), e5785. DOI
- Ln, R., Doble, M., Rekha, V.P., Pulicherla, K.K. (2011) In silico engineering of L-asparaginase to have reduced glutaminase side activity for effective treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of pediatric hematology/ oncology, 33(8), 617-621. DOI
- Ardalan, N., Akhavan, S.A., Khavari-Nejad, R. (2021) Development of Escherichia coli asparaginase II for the treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia: in silico reduction of asparaginase II side effects by a novel mutant (V27F). Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP, 22(4), 1137-1147. DOI
- Song, Z., Zhang, Q., Wu, W., Pu, Z., Yu, H. (2023) Rational design of enzyme activity and enantioselectivity. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology, 11, 1129149. DOI
- Korendovych, I.V. (2018) Rational and semirational protein design. Methods in molecular biology, 1685, 15-23. DOI
- Sellés V.L., Isalan, M., Heap, J.T., Ledesma-Amaro, R. (2023) A primer to directed evolution: current methodologies and future directions. RSC chemical biology, 4(4), 271-291. DOI
- Zeymer, C., Hilvert, D. (2018) Directed evolution of protein catalysts. Annual review of biochemistry, 87, 131-157. DOI
- Karamitros, C.S., Konrad, M. (2016) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting of human L-asparaginase mutant libraries for detecting enzyme variants with enhanced activity. ACS chemical biology, 11(9), 2596-2607. DOI
- Beckett, A., Gervais, D. (2019) What makes a good new therapeutic L-asparaginase? World journal of microbiology & biotechnology, 35(10), 152. DOI
- Lopes, W., Santos, B.A.F.D., Sampaio, A.L.F., Gregório Alves Fontão, A.P., Nascimento, H.J., Jurgilas, P.B., Torres, F.A.G., Bon, E.P.D.S., Almeida, R.V., Ferrara, M.A. (2019) Expression, purification, and characterization of asparaginase II from Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Escherichia coli. Protein expression and purification, 159, 21-26. DOI
- Ali, M., Ishqi, H.M., Husain, Q. (2020) Enzyme engineering: reshaping the biocatalytic functions. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 117(6), 1877-1894. DOI
- Pongsupasa, V., Anuwan, P., Maenpuen, S., Wongnate, T. (2021) Rationaldesign engineering to improve enzyme thermostability. Methods in molecular biology, 2397, 159-178. DOI
- Xie, W.J., Asadi, M., Warshel, A. (2022) Enhancing computational enzyme design by a maximum entropy strategy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(7), e2122355119. DOI
- Vasina, M., Velecký, J., Planas-Iglesias, J., Marques, S.M., Skarupova, J., Damborsky, J., Bednar, D., Mazurenko, S., Prokop, Z. (2022) Tools for computational design and high-throughput screening of therapeutic enzymes. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 183(1), 114143. DOI
- Chi, H., Wang, Y., Xia, B., Zhou, Y., Lu, Z., Lu, F., Zhu, P. (2022) Enhanced thermostability and molecular insights for L-asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis via structure- and computation-based rational design. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 70(45), 14499-14509. DOI
- Marcos, E., Silva, D.A. (2018) Essentials of de novo protein design: Methods and applications. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews: Computational Molecular Science, 8(6), e1374(6110). DOI
- Ferreira, P., Fernandes, P.A., Ramos, M.J. (2022) Modern computational methods for rational enzyme engineering. Chem Catalysis. 2(10), 2481-2498. DOI
- Nguyen, T.T.H., Nguyen, C. T., Nguyen, T. S.L., Du, T. T. (2016). Optimization, purification and characterization of recombinant L-asparaginase II in Escherichia coli. African Journal of Biotechnology, 15(31), 1681-1691. DOI
- Nguyen, H.A., Su, Y., Zhang, J.Y., Antanasijevic, A., Caffrey, A.M., Schalk, A., Liu, L., Rondelli, D., Oh, A., Mahmud, D.L., Bosland, M.C., Kajdacsy-Balla, A., Peirs, S., Lammens, T., Mondelaers, V., De Moerloose, B., Goossens, S., Schlicht, M.J., Kabirov, K.K., Lyubimov, A.V, Merrill, B.J., Saunthararajah, Y., Van Vlierberghe, P.V., Lavie, A. (2018) A novel L-asparaginase with low L-glutaminase coactivity is highly efficacious against both T- and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias in vivo. Cancer research, 78(6), 1549-1560. DOI
- Costa, I.M., Custódio, D., Lima, G.M., Pessoa, A., dos Santos, C.O., Oliveira, M.A., Monteiro, G. (2022). Engineered asparaginase from Erwinia chrysanthemi enhances asparagine hydrolase activity and diminishes enzyme immunoreactivity- a new promise to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 97(1), 228-239. DOI
- Linshu, J., Chi, H., Xia, B., Lu, Z., Bie, X., Zhao, H., Lu, F., Chen, M. (2022) Thermostability Improvement of L-asparaginase from Acinetobacter soli via Consensus-Designed Cysteine Residue Substitution. Molecules. 27(19), 6670. DOI
- Sudhir, A.P., Agarwaal, V.V., Dave, B.R., Patel, D.H., Subramanian, R.B. (2016) Enhanced catalysis of L-asparaginase from Bacillusl icheniformis by a rational redesign. Enzyme and microbial technology, 86, 1-6. DOI
- Zhou, Y., Jiao, L., Shen, J., Chi, H., Lu, Z., Liu, H., Lu, F., Zhu, P. (2022) Enhancing the catalytic activity of type II L-asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis through semi-rational design. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(17), 9663. DOI
- Baral, A., Gorkhali, R., Basnet, A., Koirala, S., Bhattarai, H.K. (2021) Selection of the optimal L-asparaginase II against acute lymphoblastic leukemia: an in silico approach. JMIRx Med. 2(3), e29844. DOI
- Long, S., Zhang, X., Rao, Z., Chen, K., Xu, M., Yang, T., Yang, S. (2016) Amino acid residues adjacent to the catalytic cavity of tetramer L-asparaginase II contribute significantly to its catalytic efficiency and thermostability. Enzyme and microbial technology, 82, 15-22. DOI
- Kotzia, G.A., Labrou, N.E. (2009) Engineering thermal stability of L-asparaginase by in vitro directed evolution. The FEBS journal, 276(6), 1750- 1761. DOI
- Pokrovskaya, M.V., Aleksandrova, S.S., Pokrovsky, V.S., Veselovsky, A.V., Grishin D.V., Abakumova, O.Y., Podobed, O.V., Mishin, A.A., Zhdanov, D.D., Sokolov, N.N. (2015) Identification of functional regions in the Rhodospirillum rubrum L-asparaginase by site-directed mutagenesis. Molecular Biotechnology, 57(3), 251-264. DOI
- Lu, X., Chen, J., Jiao, L., Zhong, L., Lu, Z., Zhang, C., Lu, F. (2019) Improvement of the activity of L-asparaginase I improvement of the catalytic activity of L-asparaginase I from Bacillus megaterium H-1 by in vitro directed evolution. Journal of bioscience and bioengineering, 128(6), 683-689. DOI
- Aghaeepoor, M., Akbarzadeh, A., Mirzaie, S., Hadian, A., Jamshidi Aval, S., Dehnavi, E. (2018) Selective reduction in glutaminase activity of L-Asparaginase by asparagine 248 to serine mutation: A combined computational and experimental effort in blood cancer treatment. International journal of biological macromolecules, 120(Pt B), 2448-2457. DOI
- Faber, M.S, Whitehead, T.A. (2019) Data-driven engineering of protein therapeutics. Current opinion in biotechnology, 60, 104-110. DOI
- Sannikova, E.P., Bulushova, N.V., Cheperegin, S.E., Gubaydullin, I.I., Chestukhina, G.G., Ryabichenko, V.V., Zalunin, I.A., Kotlova, E.K., Konstantinova, G.E., Kubasova, T.S., Shtil, A.A, Pokrovsky, V.S., Yarotsky, S.V., Efremov, B.D., Kozlov, D.G. (2016) The modified heparin-binding L-asparaginase of Wolinella succinogenes. Molecular biotechnology, 58(8-9), 528-539. DOI
- Belén, L.H., Lissabet, J.B., de Oliveira Rangel-Yagui, C., Effer, B., Monteiro, G., Pessoa, A., Farías Avendaño, J.G. (2019) A structural in silico analysis of the immunogenicity of L-asparaginase from Escherichia coli and Erwinia carotovora. Biologicals: journal of the International Association of Biological Standardization 59, 47-55. DOI
- Cantor, J.R., Yoo, T.H., Dixit, A., Iverson, B.L., Forsthuber, T.G., Georgiou, G. (2011) Therapeutic enzyme deimmunization by combinatorial T-cell epitope removal using neutral drift. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(4), 1272-1277. DOI
- Cantor, J.R., Panayiotou, V., Agnello, G., Georgiou, G., Stone, E.M. (2012) Engineering reduced-immunogenicity enzymes for amino acid depletion therapy in cancer. Methods in enzymology, 502, 291-319. DOI
- Alexandrova, S.S., Gladilina, Y.A., Pokrovskaya, M.V., Sokolov, N.N., Zhdanov D.D. (2022) Mechanisms of development of side effects and drug resistance to L-asparaginase and ways to overcome them. Biomeditsinskaia khimiia, 68(2), 104-116. DOI
- Pokrovskaya, M.V., Zhdanov, D.D., Eldarov, M.A., Aleksandrova, S.S., Veselovskiy, A.V., Pokrovskiy, V.S., Grishin, D.V., Gladilina, J.A., Sokolov, N.N. (2017) Suppression of telomerase activity leukemic cells by mutant forms of Rhodospirillum rubrum L-asparaginase. Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya, 63(1), 62-74. DOI
- Gupta, S.K., Shukla, P. (2016) Advanced technologies for improved expression of recombinant proteins in bacteria: perspectives and applications. Critical reviews in biotechnology, 36(6), 1089-1098. DOI
- Kant Bhatia, S., Vivek, N., Kumar, V., Chandel, N., Thakur, M., Kumar, D., Yang, Y., Pugazendhi, A., Kumar, G. (2021) Molecular biology interventions for activity improvement and production of industrial enzymes. Bioresource technology, 324, 124596. DOI
- Rieder, L., Teuschler, N., Ebner, K., Glieder, A. (2019). Eukaryotic expression systems for industrial enzymes. In Industrial Enzyme Applications (A. Vogel and O. May eds.)Wiley-VCH, pp. 47-69. DOI
- Terpe, K. (2006) Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Applied microbiology and biotechnology. 72(2), 211- 222. DOI
- Datar, R.V., Cartwright, T., Rosen, C.G. (1993) Process economics of animal cell and bacterial fermentations: a case study analysis of tissue plasminogen activator. Biotechnology (N Y), 11(3), 349-357. DOI
- John, N. Abelson, David V. Goeddel, Melvin I. Simon (1990) Gene expression technology. In methods in enzymology, ( David V. Goeddel Ed.) Academic Press, San Diego, 185, pp. 3-681
- Dell, A., Galadari, A., Sastre, F., Hitchen, P. (2010) Similarities and differences in the glycosylation mechanisms in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. International journal of microbiology, 2010, 148178. DOI
- Varki, A. (1993) Biological roles of oligosaccharides: all of the theories are correct. Glycobiology, 3(2), 97-130. DOI
- Withka, J.M., Wyss, D.F., Wagner, G., Arulanandam, A.R., Reinherz, E.L., Recny, M.A. (1993) Structure of the glycosylated adhesion domain of human T lymphocyte glycoprotein CD2. Structure (London, England), 1(1), 69-81. DOI
- Elliott, S., Lorenzini, T., Asher, S., Aoki, K., Brankow, D., Buck, L., Busse, L., Chang, D., Fuller, J., Grant, J., Hernday, N., Hokum, M., Hu, S., Knudten, A., Levin, N., Komorowski, R., Martin, F., Navarro, R., Osslund, T., Rogers, G., Rogers, N., Trail, G., Egrie, J. (2003) Enhancement of therapeutic protein in vivo activities through glycoengineering. Nature biotechnology, 21(4), 414-421. DOI
- Flintegaard, T.V., Thygesen, P., Rahbek-Nielsen, H., Levery, S.B., Kristensen, C., Clausen, H., Bolt, G. (2010) N-glycosylation increases the circulatory half-life of human growth hormone. Endocrinology, 151(11), 5326- 5336. DOI
- Solá, R.J., Griebenow, K. (2009) Effects of glycosylation on the stability of protein pharmaceuticals. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 98(4), 1223-1245. DOI
- Sadoulet, M.O., Franceschi, C., Aubert, M., Silvy, F., Bernard, J.P., Lombardo, D., Mas, E. (2007) Glycoengineering of alpha Gal xenoantigen on recombinant peptide bearing the J28 pancreatic oncofetal glycotope. Glycobiology, 17(6), 620-630. DOI
- Wacker, M., Wang, L., Kowarik, M., Dowd, M., Lipowsky, G., Faridmoayer, A., Shields, K., Park, S., Alaimo, C., Kelley, K.A., Braun, M., Quebatte, J., Gambillara, V., Carranza, P., Steffen, M., Lee, J.C. (2014) Prevention of Staphylococcus aureus infections by glycoprotein vaccines synthesized in Escherichia coli. The Journal of infectious diseases, 209(10), 1551-1561. DOI
- Sinclair, A.M., Elliott, S. (2005) Glycoengineering: the effect of glycosylation on the properties of therapeutic proteins. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 94(8), 1626-1635. DOI
- Feige, M.J., Braakman, I., Hendershot, L.M. (2018) Disulfide bonds in protein folding and stability. In oxidative folding of proteins: basic principles, cellular regulation and engineering, (M. J. Feige ed.) The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1-33. DOI
- Thornton, J.M. (1981) Disulphide bridges in globular proteins. Journal of molecular biology, 151(2), 261-287. DOI
- Ferrara, M.A., Severino, N.M.B., Mansure, J.J., Martins, A.S., Oliveira, E., Siani, A.C., Jr, N.P., Torres, F.A., Bon,E.P.S. (2006) Asparaginase production by a recombinant Pichia pastoris strain harbouring Saccharomyces cerevisiae ASP3 gene. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 39 (7), 1457-1463. DOI
- Vittaladevaram, V. (2021) A Short communication on Pichia pastorisi vs. E. coli: Efficient expression system. Annals of Proteomics and Bioinformatics, 5(1), 49-50. DOI
- Jacobs, P., Geysens, S., Vervecken, W., Contreras, R.H., Callewaert, N. (2009) Engineering complex-type N-glycosylation in Pichia pastoris using GlycoSwitch technology. Nature protocols, 4(1), 58-70. DOI
- Pan, Y., Yang, J., Wu, J., Yang, L., Fang, H. (2022) Current advances of Pichia pastoris as cell factories for production of recombinant proteins. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13(1), 1059777. DOI
- Juturu, V., Wu, J.C (2018) Heterologous protein expression in Pichia pastoris: latest research progress and applications. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 19(1), 7-21. DOI
- Ahmad, M., Hirz, M., Pichler, H., Schwab, H. (2014) Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 98(12), 5301-5317. DOI
- Rodrigues, D., Pillaca-Pullo, O., Torres-Obreque, K., Flores-Santos, J., Sánchez-Moguel, I., Pimenta, M.V., Basi, T., Converti, A., Lopes, A.M., Monteiro, G., Fonseca, L.P., Pessoa, A.J. (2019) Fed-batch production of Saccharomyces cerevisiae L-asparaginase II by recombinant Pichia pastoris MUTs strain. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology, 7, 16. DOI
- Karbalaei, M., Rezaee, S.A., Farsiani, H. (2020) Pichia pastoris: A highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins. Journal of cellular physiology, 235(9), 5867-5881. DOI
- Parizotto, L., Kleingesinds, E., da Rosa, L.M.P., Roldán E.B., Lima, G.M., Herkenhoff, M.E., Li, Z., Rinas, U., Monteiro, G., Pessoa, A., Tonso, A. (2021) Increased glycosylated L-asparaginase production through selection of Pichia pastoris platforma and oxygen-methanol control in fed-batches. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 173, 108083. DOI
- Lima, G.M., Roldán, B.E., Biasoto, H.P., Feijoli, V., Pessoa, A., Palmisano, G., Monteiro, G. (2020) Glycosylation of L-asparaginase from E. coli through yeast expression and site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemical Engineering Journal. 156, 107516. DOI
- Nguyen, T.C., Nguyen, T.T.H., Tuyen, Do.T., Thi, Quyen D.T.(2014). Expression, purification and evaluation of recombinant L-asparaginase in menthylotrophic Pichia pastoris. Journal of Vietnamese Environment, 6(3), 288-292. DOI
- Effer, B., Kleingesinds, E.K., Lima, G.M., Costa, I.M., Sánchez-Moguel, I., Pessoa, A., Santiago, V.F., Palmisano, G., Farías, J.G., Monteiro, G. (2020) Glycosylation of Erwinase results in active protein less recognized by antibodies. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 163(301), 107750. DOI
- Sajitha, S., Vidya, J., Varsha, Karunakaran , Binod, P., Pandey, A. (2015) Cloning and expression of L-asparaginase from E.coli in eukaryotic expression system. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 102, 14-17. DOI
- Dantas, R.C, Caetano, L.F., Torres, A.L.S., Alves, M.S., Silva, E.T.M.F., Teixeira, L.P.R., Teixeira, D.C., de Azevedo Moreira, R., Fonseca, M.H.G., Gaudêncio Neto, Martins, L.T., Furtado, G.P., Tavares, K.C.S. (2019) Expression of a recombinant bacterial L-asparaginase in human cells. BMC research notes, 12(1), 794. DOI
- Gupta, R., Jung, E., Brunak, S. (2004). Prediction of N-glycosylation sites in human proteins. In: Preparation, 46, 203-206
- Zhou, Q., Qiu, H. (2019) The Mechanistic impact of N-glycosylation on stability, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 108(4), 1366-1377. DOI
- Gribben, J.G., Devereux, S., Thomas, N.S., Keim, M., Jones, H.M., Goldstone, A.H., Linch, D.C. (1990) Development of antibodies to unprotected glycosylation sites on recombinant human GM-CSF. Lancet, 335(8687), 434- 437. DOI
- Hermeling, S., Crommelin, D.J., Shellekens, H., Jiskoot, W. (2004) Structure-immunogenicity relationships of therapeutic proteins. Pharmaceutical Research, 21(6), 897-903, DOI
- Pouresmaeil, M., Azizi-Dargahlou, S. (2023) Factors involved in heterologous expression of proteins in E. coli host. Archives of microbiology, 205(5), 212. DOI
- Khushoo, A., Pal, Y., Mukherjee, K.J. (2005) Optimization of extracellular production of recombinant asparaginase in Escherichia coli in shake-flask and bioreactor. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 68(2), 189-197. DOI
- Rosano, G.L., Ceccarelli, E.A. (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5(172), 172. DOI
- Derman, A.I., Prinz, W.A., Belin, D., Beckwith, J. (1993) Mutations that allow disulfide bond formation in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Science, 262(5140), 1744-1747. DOI
- Wang, Y., Qian, S., Meng, G., Zhang, S. (2001) Cloning and expression of L-asparaginase gene in Escherichia coli. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 95(2), 93-101. DOI
- Goswami, R., Hegde, K., Dasu, V. V.(2015) Production and characterization of novel glutaminase free recombinant L-asparaginase II of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica SCRI 1043 in E. coli BL21 (DE3). British Microbiology Research Journal. 6(2), 95-112. DOI
- Chand, S., Mahajan, R.V., Prasad, J.P., Sahoo, D.K., Mihooliya, K.N., Dhar, M.S., Sharma, G. (2020) A comprehensive review on microbial L-asparaginase: Bioprocessing, characterization, and industrial applications. Biotechnology and applied biochemistry, 67(4), 619-647. DOI
- Chi, H., Chen, M., Jiao, L., Lu, Z., Bie, X., Zhao, H., Lu, F. (2021) Characterization of a novel L-asparaginase from Mycobacterium gordonae with acrylamide mitigation potential. Foods, 10(11), 2819. DOI
- Pourhossein, M., Korbekandi, H. (2014) Cloning, expression, purification and characterisation of Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase in Escherichia coli. Advanced biomedical research, 3(1), 82. DOI
- Dumina, M.V., Zhgun, A.A., Pokrovskaya, M.V., Aleksandrova, S.S., Zhdanov, D.D., Sokolov, N.N., El’darov, M.A. (2021) Comparison of enzymatic activity of novel recombinant L-asparaginases of extremophiles. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 57(5), 594-602. DOI
- Abdullah, E. M., Khan, M. S., Aziz, I. M., Alokail, M. S., Karthikeyan, S., Rupavarshini, M., Bhat, S. A., Ataya, F. S. (2024). Expression, characterization and cytotoxicity of recombinant l-asparaginase II from Salmonella paratyphi cloned in Escherichia coli. International journal of biological macromolecules, 279(Pt 4), 135458. DOI
- Dumina, M., Zhgun, A., Pokrovskaya, M., Aleksandrova, S., Zhdanov, D., Sokolov, N., El’darov, M. (2021) A novel L-asparaginase from hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus sibiricus: heterologous expression and characterization for biotechnology application. International journal of molecular sciences, 22(18), 9894. DOI
- Farahat, M.G., Amr, D., Galal, A. (2020) Molecular cloning, structural modeling and characterization of a novel glutaminase-free L-asparaginase from Cobetia amphilecti AMI6. International journal of biological macromolecules, 143, 685-695. DOI
- Kumar, V., Kumar, R., Sharma, S., Shah, A., Prakash Chaturvedi, C., Verma., D. (2024) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel thermoacidophilic l-asparaginase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa CSPS4. 3 Biotech 14, 54 . DOI
- Izadpanah Qeshmi, F., Homaei, A., Khajeh, K., Kamrani, E., Fernandes, P. (2022) Production of a novel marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant L-asparaginase: insight on the structure and biochemical characterization. Marine Biotechnology, 24(3), 599-613. DOI
- Karamitros, C.S., Labrou, N. (2014). Extracellular expression and affinity purification of L-asparaginase from E. chrysanthemi in E. coli. Sustainable Chemical Processes, 2(1), 16. DOI
- Meena, B., Anburajan, L., Sathish, T., Vijaya, Raghavan, R., Dharani, G., Vinithkumar, N.V., Kirubagaran, R. (2015) L-Asparaginase from Streptomyces griseus NIOT-VKMA29: optimization of process variables using factorial designs and molecular characterization of L-asparaginase gene. Scientific reports, 5(1), 12404. DOI
- Meena, B., Anburajan, L., Dheenan, P.S., Begum, M., Vinithkumar, N.V., Dharani, G., Kirubagaran, R. (2015) Novel glutaminase free L-asparaginase from Nocardiopsis alba NIOT-VKMA08: production, optimization, functional and molecular characterization. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 38(2), 373-388. DOI
- Meena, B., Anburajan, L., Vinithkumar, N.V., Shridhar, D., Raghavan, R.V., Dharani, G., Kirubagaran, R. (2016) Molecular expression of L-asparaginase gene from Nocardiopsis alba NIOT-VKMA08 in Escherichia coli: A prospective recombinant enzyme for leukaemia chemotherapy. Gene, 590(2), 220-226. DOI
- Hegazy, W., Abdel-Salam, M.S., Moharam, M. (2020). Biotechnological approach for the production of L-asparaginase from locally Bacillus subtilis isolate. Egyptian Pharmaceutical Journal. 19(2), 155-161. DOI
- de Moura, W.A.F., Schultz, L., Breyer, C.A., de Oliveira A.L.P., Tairum, C.A., Fernandes, G.C., Toyama, M.H., Pessoa-Jr, A., Monteiro, G., de Oliveira, M.A. (2020) Functional and structural evaluation of the antileukaemic enzyme L-asparaginase II expressed at low temperature by different Escherichia coli strains. Biotechnology letters, 42(11), 2333-2344. DOI
- Kotzia, G.A., Labrou, N.E. (2007) L-asparaginase from Erwinia Chrysanthemi 3937: cloning, expression and characterization. Journal of biotechnology, 127(4), 657-669. DOI
- Saeed, H., Hemida, A., El-Nikhely, N., Abdel-Fattah, M., Shalaby, M., Hussein, A., Eldoksh, A., Ataya, F., Aly, N., Labrou, N., Nematalla, H. (2020) Highly efficient Pyrococcus furiosus recombinant L-asparaginase with no glutaminase activity: Expression, purification, functional characterization, and cytotoxicity on THP-1, A549 and Caco-2 cell lines. International journal of biological macromolecules, 156(3), 812-828. DOI
- Chohan, S.M., Rashid, N., Sajed, M., Imanaka, T. (2019) Pcal_0970: an extremely thermostable L-asparaginase from Pyrobaculum calidifontis with no detectable glutaminase activity. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 64(3), 313-320. DOI
- Souza, C.C., Guimarães, J.M., Pereira, S.D.S., Mariúba, L.A.M. (2021) The multifunctionality of expression systems in Bacillus subtilis: Emerging devices for the production of recombinant proteins. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.), 246(23), 2443-2453. DOI
- Gomes, A.R., Byregowda, S.M., Veeregowda, B.M., Vinayagamurthy, Balamurugan. (2016). An Overview of heterologous expression host systems for the production of recombinant proteins. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 4(7), 346-356. DOI
- Niu, J., Meng, F., Zhou, Y., Zhang, C., Lu, Z., Lu, F., Chen, M. (2021). Nonclassical secretion of a type I L-asparaginase in Bacillus subtilis. International journal of biological macromolecules, 180, 677-683. DOI
- Yang, H., Qu, J., Zou, W., Shen, W., Chen, X. (2021) An overview and future prospects of recombinant protein production in Bacillus subtilis. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 105(18), 6607-6626. DOI
- Cui, W., Han, L., Suo, F., Liu, Z., Zhou, L., Zhou, Z. (2018) Exploitation of Bacillus subtilis as a robust workhorse for production of heterologous proteins and beyond. World journal of microbiology & biotechnology, 34(10), 145. DOI
- Bento, H.B.S., Paiva, G.B., Almeida, M.R., Silva, C.G., Carvalho, P.J., Tavares, A.P.M., Pedrolli, D.B., Santos-Ebinuma, V.C. (2022) Aliivibrio fischeri L-asparaginase production by engineered Bacillus subtilis: a potential new biopharmaceutical. Bioprocess and biosystems engineering, 45(10), 1635-1644. DOI
- Li, X., Zhang, X., Xu, S., Zhang, H., Xu, M., Yang, T., Wang, L., Qian, H., Zhang, H., Fang, H., Osire, T., Rao, Z., Yang, S. (2018) Simultaneous cell disruption and semi-quantitative activity assays for high-throughput screening of thermostable L-asparaginases. Scientific reports, 8(1), 7915. DOI
- Chityala, S., Venkata Dasu, V., Ahmad, J., Prakasham, R.S. (2015) High yield expression of novel glutaminase free L-asparaginase II of Pectobacterium carotovorum MTCC 1428 in Bacillus subtilis WB800N. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 38(11), 2271-2284. DOI
- Feng, Y., Liu, S., Jiao, Y., Gao, H., Wang, M., Du, G., Chen, J. (2017) Enhanced extracellular production of L-asparaginase from Bacillus subtilis 168 by B. subtilis WB600 through a combined strategy. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 101(4), 1509-1520. DOI
- Boni, I.V., Isaeva, D.M., Musychenko, M.L., Tzareva, N.V. (1991) Ribosome-messenger recognition: mRNA target sites for ribosomal protein S1. Nucleic acids research, 19(1), 155-162. DOI
- Oza, V.P., Parmar, P.P., Patel, D.H., Subramanian, R.B. (2011) Cloning, expression and characterization of L-asparaginase from Withania somnifera L. for large scale production. 3 Biotechnology, 1(1), 21-26. DOI
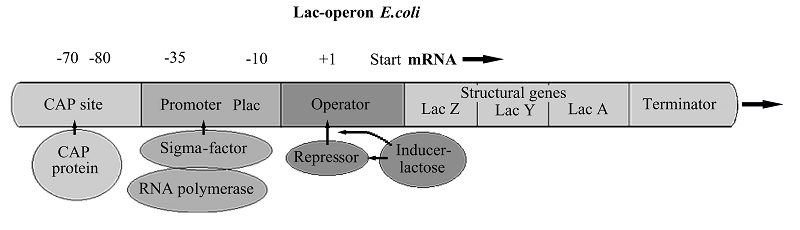
- Jacob, F., Monod, J. (1961) Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. Journal of molecular biology, 3, 318–356. DOI
- Duzenli, O.F., Okay, S. (2020) Promoter engineering for the recombinant protein production in prokaryotic systems. AIMS Bioengineering, 7(2), 62-81. DOI
- Deuschle, U., Kammerer, W., Gentz, R., Bujard, H. (1986) Promoters of Escherichia coli: a hierarchy of in vivo strength indicates alternate structures. The EMBO journal, 5(11), 2987-2994. DOI
- Gaal, T., Barkei, J., Dickson, R.R., de Boer, H.A., de Haseth, P.L., Alavi, H., Gourse, R.L. (1989) Saturation mutagenesis of an Escherichia coli rRNA promoter and initial characterization of promoter variants. Journal of bacteriology, 171(9), 4852-4861. DOI
- Hsu, L.M., Giannini, J.K., Leung, T.W., Crosthwaite, J.C. (1991) Upstream sequence activation of Escherichia coli argT promoter in vivo and in vitro. Biochemistry, 30(3), 813-822. DOI
- Josaitis, C.A., Gaal, T., Ross, W., Gourse, R. L. (1990) Sequences upstream of the-35 hexamer of rrnB P1 affect promoter strength and upstream activation. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1050(1-3), 307-311. DOI
- Zacharias, M., Göringer, H.,U. Wagner, R. (1992) Analysis of the Fisdependent and Fis-independent transcription activation mechanisms of the Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA P1 promoter. Biochemistry. 31(9), 2621-2628. DOI
- Rao, L., Ross, W., Appleman, J.A., Gaal, T., Leirmo, S., Schlax, P.J., Record, M.T., Jr., Gourse, R.L. (1994) Factor independent activation of rrnB P1. An “extended” promoter with an upstream element that dramatically increases promoter strength. Journal of molecular biology, 235(5), 1421-1435. DOI
- Ross, W., Gosink, K.,K., Salomon, J., Igarashi, K., Zou, C., Ishihama, A., Severinov, K., Gourse, R.L. (1993) A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science, 262(5138), 1407-1413. DOI
- Lisser, S., Margalit, H. (1993) Compilation of E. coli mRNA promoter sequences. Nucleic acids research, 21(7), 1507-1516. DOI
- Darwesh, D.B., Al-Awthan, Y.S., Elfaki, I., Habib, S.A., Alnour, T.M., Darwish, A.B., Youssef, M.M. (2022) Anticancer Activity of Extremely Effective Recombinant L-Asparaginase from Burkholderia pseudomallei. Journal of microbiology and biotechnology, 325(5), 551-563. DOI
- Saeed, H., Hemida, A., Abdel-Fattah, M., Eldoksh, A., Shalaby, M., Nematalla, H., El-Nikhely, N., Elkewedi, M. (2021) Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant L-asparaginase: Large scale production, purification, and cytotoxicity on THP-1, MDA-MB-231, A549, Caco2 and HCT-116 cell lines. Protein expression and purification, 181(2C), 105820. DOI
- Wang, Y., Liu, Q., Weng, H., Shi, Y., Chen, J., Du, G., Kang, Z. (2019) Construction of synthetic promoters by assembling the sigma factor binding -35 and -10 Boxes. Biotechnology journal, 14(1):e1800298. DOI
- Lozano Terol, G., Gallego-Jara, J., Sola Martínez, R.A., Martínez Vivancos, A., Cánovas Díaz, M., de Diego Puente, T. (2021) Impact of the expression system on recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli BL21. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 682001. DOI
- Ehl’darov, M. A., Zhgun, A.A.,Gervaziev, J.V., Aleksandrova, S.S.,Omel’janjuk, N.M., Archakov, A.I. Skrjabin, K.G., Sokolov, N.N. Gene encoding L-asparaginase in Erwinia Carotovora and strain Escherichia coli VKPM = B-8174 as producer of Erwinia Carotovora L-asparaginase (Patent No. RF №2221868,МПКC12N, 2004).
- Jayapal, K.P., Lian, W., Glod, F., Sherman, D.H., Wei-Shou Hu, W.S. Comparative genomic hybridizations reveal absence of large Streptomyces coelicolor genomic islands in Streptomyces lividans. BMC Genomics 8, 229 (2007). DOI
- Roth, G., Nunes, J.E.S., Rosado, L.A., Bizarro, C., Volpato, G., Nunes, C.P., Renard, G., Basso, L.A., Santos, D.S., Chies, J.M. (2013) Recombinant Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase II production in Escherichia coli fed-batch cultures. Brazilian journal of chemical engineering, 30(2), 245-256. DOI
- Lee, G., Saito, I. (1998) Role of nucleotide sequences of loxP spacer region in Cre-mediated recombination. Gene. 216(1), 55-65. DOI
- Turan, S., Kuehle, J., Schambach, A., Baum, C., Bode, J. (2010) Multiplexing RMCE: versatile extensions of the Flp-recombinase-mediated cassette-exchange technology. Journal of molecular biology, 402(1), 52-69. DOI
- Turan, S., Galla, M., Ernst, E., Qiao, J., Voelkel, C., Schiedlmeier, B., Zehe, C., Bode, J. (2011) Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE): traditional concepts and current challenges. Journal of molecular biology, 407(2), 193-221. DOI
- Wang, Y., Yau, Y., Perkins-Balding, D., Thomson, J. (2011) Recombinase technology: applications and possibilities. Plant cell reports, 30(3), 267-285. DOI
- Schalk, A.M., Nguyen H.A., Rigouin, C., Lavie , A. ( 2014) Identification and Structural Analysis of an l-Asparaginase Enzyme from Guinea Pig with Putative Tumor Cell Killing Properties Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(48), 33175-33186. DOI
- Sajed, M., Falak, S., Muhammad, M.A., Ahmad, N., Rashid, N. (2022). A plant-type L-asparaginase from Pyrobaculum calidifontis undergoes temperature dependent autocleavage. Biologia, 77(12), 1-9. DOI
- Jia, M., Xu, M., He, B., Rao, Z. (2013) Cloning, expression, and characterization of L-asparaginase from a newly isolated Bacillus subtilis B11- 06. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 61(39), 9428-9434. DOI
- Urnov, F.D., Rebar, E.J., Holmes, M.C., Zhang, H.S., Gregory, P.D. (2010) Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nature reviews. Genetics, 11(9), 636-646. DOI
- Carroll, D. (2011) Genome engineering with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics, 188(4), 773-782. DOI
- Christian, M., Cermak, T., Doyle, E.L., Schmidt, C., Zhang, F., Hummel, A., Bogdanove, A.J., Voytas, D.F. (2010) Targeting DNA double-strand breaks with TAL effector nucleases. Genetics, 186(2), 757-761. DOI
- Christian, M., Voytas, D.F. (2015). Engineered TAL effector proteins: versatile reagents for manipulating plant genomes. In Advances in new technology for targeted modification of plant genomes. (Zhang, F., Puchta, H., Thomson, J. eds) New York, NY.pp. 55-72. DOI
- Sun, N., Zhao, H. (2013) Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs): a highly efficient and versatile tool for genome editing. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 110(7), 1811-1821. DOI
- Alba Burbano, D., Cardiff, R.A.L., Tickman, B.I., Kiattisewee, C., Maranas, C.J., Zalatan, J.G., Carothers, J.M. (2023) Engineering activatable promoters for scalable and multi-input CRISPRa/i circuits. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 120(30), e2220358120. DOI
- Makarova, K.S., Haft, D.H., Barrangou, R., Brouns, S.J., Charpentier, E., Horvath, P., Moineau, S., Mojica, F.J., Wolf, Y.I., Yakunin, A.F., van der Oost, J., Koonin, E.V. (2011) Evolution and classification of the CRISPR-Cas systems. Nature reviews. Microbiology, 9(6), 467-477. DOI
- Cong, L., Ran, F.A., Cox, D., Lin, S., Barretto, R., Habib, N., Hsu, P.D., Wu, X., Jiang, W., Marraffini, L.A., Zhang, F. (2013) Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science, 339(6121), 819-823. DOI
- Ran, F.A., Hsu, P.D., Wright, J., Agarwala, V., Scott, D.A., Zhang, F. (2013) Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nature protocols, 8(11), 2281-2308. DOI
- Hsu, P.D., Lander, E.S., Zhang, F. (2014) Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell, 157(6), 1262-1278. DOI
- Jinek, M., Chylinski, K., Fonfara, I., Hauer, M., Doudna, J.A., Charpentier, E. (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science, 337(6096), 816-821. DOI
- Brazelton, V.A., Jr, Zarecor, S., Wright, D.A., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Chen, K., Yang, B., Lawrence-Dill, C.J. (2015) A quick guide to CRISPR sgRNA design tools. GM crops food, 6(4), 266-276. DOI
- Sahel, D.K., Vora, L.K., Saraswat, A., Sharma, S., Monpara, J., D’Souza, A.A., Mishra, D., Tryphena, K.P., Kawakita, S., Khan, S., Azhar, M., Khatri, D.K., Patel, K., Singh Thakur, R.R. (2023) CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing for Tissue-Specific In Vivo Targeting: Nanomaterials and Translational Perspective. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), 10(19), e2207512. DOI
- Bannikov, A.V., Lavrov, A.V. (2017) CRISPR/CAS9, the King of Genome Editing Tools. Molekuliarnaia biologiia, (Mosk). 51(4), 582-594. DOI
- Fontana, J., Sparkman-Yager, D., Zalatan, J.G., Carothers, J.M. (2020) Challenges and opportunities with CRISPR activation in bacteria for datadriven metabolic engineering. Current opinion in biotechnology, 64, 190-198. DOI
- Costa, I. M., Effer, B., Costa-Silva, T. A., Chen, C., Ciccone, M. F., Pessoa, A., Dos Santos, C. O., Monteiro, G. (2023). Cathepsin B Is Not an Intrinsic Factor Related to Asparaginase Resistance of the Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia REH Cell Line. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(13), 11215. DOI
- Weninger, A., Hatzl, A.M., Schmid, C., Vogl, T., Glieder, A. (2016). Combinatorial optimization of CRISPR/Cas9 expression enables precision genome engineering in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Journal of Biotechnology, 235, 139-149. DOI
- Gu, Y., Xu, X., Wu, Y., Niu, T., Liu, Y., Li, J., Du, G., Liu, L. (2018) Advances and prospects of Bacillus subtilis cellular factories: From rational design to industrial applications. Metabolic engineering, 50, 109-121. DOI
- Gao, J., Jiang, L., Lian, J. (2021) Development of synthetic biology tools to engineer Pichia pastoris as a chassis for the production of natural products. Synthetic and systems biotechnology, 6(2), 110-119. DOI
- Thor, D., Xiong, S., Orazem, C.C., Kwan, A.C., Cregg, J.M., Lin- Cereghino, J., Lin-Cereghino, G.P. (2005) Cloning and characterization of the Pichia pastoris MET2 gene as a selectable marker. FEMS yeast research, 5(10), 935-942. DOI
- Piva, L.C., Bentacur, M.O., Reis, V.C.B., De Marco, J.L., Moraes, L.M.P., Torres, F.A.G. (2017) Molecular strategies to increase the levels of heterologous transcripts in Komagataella phaffii for protein production. Bioengineered, 8(5), 441-445. DOI
- Das, A. (1990) Overproduction of proteins in Escherichia coli: vectors, hosts, and strategies. Methods in enzymology, 182, 93-112. DOI
- Balbas, P., Bolivar, F. (1990) Design and construction of expression plasmid vectors in Escherichia coli. Methods in enzymology, 185, 14-37. DOI
- Brosius, J. (1992) Compilation of superlinker vectors. Methods in enzymology, 216, 469-483. DOI
- MacFerrin, K.D., Chen, L., Terranova, M.P., Schreiber, S.L., Verdine, G.L. (1993) Overproduction of proteins using expression-cassette polymerase chain reaction. Methods in enzymology, 217, 79-102. DOI
- Yansura, D.G., Henner, D.J. (1990) Use of Escherichia coli trp promoter for direct expression of proteins. Methods in enzymology, 185, 54-60. DOI
- Anné, J., Economou, A., Bernaerts, K. (2017) Protein Secretion in Gram- Positive Bacteria: From Multiple Pathways to Biotechnology. Current topics in microbiology and immunology, 404, 267-308. DOI
- Sambrook, J., Russell, D. (2012) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed., Vols 1,2 and 3 ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2100 pp.
- Walker J.M., Ralph Rapley (2000) Molecular biology and biotechnology. The royal society of chemistry , London. DOI
- Huang, L., Liu, Y., Sun, Y., Yan, Q., Jiang, Z. (2014) Biochemical characterization of a novel L-asparaginase with low glutaminase activity from Rhizomucor miehei and its application in food safety and leukemia treatment. Applied and environmental microbiology, 80(5), 1561-1569. DOI
- Labes, M., Pühler, A., Simon, R. (1990) A new family of RSF1010-derived expression and lac-fusion broad-host-range vectors for gram-negative bacteria. Gene, 89(1), 37-46. DOI
- Balbas, P., Soberon, X., Bolivar, F., Rodriguez, R.L. (1988). The plasmid, pBR322. Biotechnology, 10, 5-41. DOI
- Li, P., Anumanthan, A., Gao, X.G., Ilangovan, K., Suzara, V.V., Düzgüneş, N., Renugopalakrishnan, V. (2007) Expression of recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 142(2), 105-124. DOI
- de Boer, H.A., Comstock, L.J., Vasser, M. (1983) The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 80(1), 21-25. DOI
- Hayat, S.M.G., Farahani, N., Golichenari, B., Sahebkar A.H. (2018) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli (E. coli): What We Need to Know. Current pharmaceutical design, 24(6), 718-725. DOI
- San, K.Y., Bennett, G.N., Chou, C.H., Aristidou, A.A. (1994) An optimization study of a pH-inducible promoter system for high-level recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Annals of the New York academy of sciences, 721, 268-276. DOI
- Chou, C.H., Aristidou, A.A., Meng, S.Y., Bennett, G.N., San, K.Y. (1995) Characterization of a pH-inducible promoter system for high-level expression of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 47(2), 186-192. DOI
- Tolentino, G.J., Meng, S.Y., Bennett, G.N., San, K.Y. (1992) A pH-regulated promoter for the expression of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology letters, 14, 157-162. DOI
- Giladi, H., Goldenberg, D., Koby, S., Oppenheim, A.B. (1995) Enhanced activity of the bacteriophage lambda PL promoter at low temperature. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92(6), 2184-2188. DOI
- Tanabe, H., Goldstein, J., Yang, M., Inouye, M. (1992) Identification of the promoter region of the Escherichia coli major cold shock gene, cspA. Journal of bacteriology, 174(12), 3867-3873. DOI
- Oppenheim, A.B., Giladi, H., Goldenberg, D., S. Kobi, S., Azar, I. (1996) Vectors and transformed host cells for recombinant protein production at reduced temperatures. International patent application patent/US5726039A
- Goldstein, M.A., Doi, R.H. (1995) Prokaryotic promoters in biotechnology. Biotechnology annual review, 1, 105-128. DOI
- Bentley, W.E., Mirjalili, N., Andersen, D.C., Davis, R.H., Kompala, D.S. (1990) Plasmid-encoded protein: the principal factor in the “metabolic burden” associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 35(7), 668-681. DOI
- Minas, W., Bailey, J.E. (1995) Co-overexpression of prlF increases cell viability and enzyme yields in recombinant Escherichia coli expressing Bacillus stearo thermophilus alpha-amylase. Biotechnology progress, 11(4), 403-411. DOI
- Chen, W., Kallio, P.T., Bailey, J.E. (1995) Process characterization of a novel cross-regulation system for cloned protein production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology progress, 11(4), 397-402. DOI
- Mertens, N., Remaut, E., Fiers, W. (1995) Tight transcriptional control mechanism ensures stable high-level expression from T7 promoter-based expression plasmids. Biotechnology (N Y), 13(2), 175-179. DOI
- Depicker, A., Montagu, M.V. (1997) Post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants. Current opinion in cell biology, 9(3), 373-382. DOI
- O’Connor, C.D., Timmis, K.N. (1987) Highly repressible expression system for cloning genes that specify potentially toxic proteins. Journal of bacteriology, 169(10), 4457-4462. DOI
- Brown, W.C., Campbell, J.L. (1993) A new cloning vector and expression strategy for genes encoding proteins toxic to Escherichia coli. Gene, 127(1), 99-103. DOI
- Doherty, A.J., Connolly, B.A., Worrall, A.F. (1993) Overproduction of the toxic protein, bovine pancreatic DNaseI, in Escherichia coli using a tightly controlled T7-promoter-based vector. Gene.136(1-2), 337-340. DOI
- Suter-Crazzolara, C., Unsicker, K. (1995) Improved expression of toxic proteins in E. coli. Biotechniques, 19(2), 202-204; ISSN: 0736-6205
- Trudel, P., Provost, S., Massie, B., Chartrand, P., Wall, L. (1996) pGATA: a positive selection vector based on the toxicity of the transcription factor GATA- 1 to bacteria. Biotechniques, 20(4), 684-693. DOI
- Wülfing, C., Plückthun, A. (1993) A versatile and highly repressible Escherichia coli expression system based on invertible promoters: expression of a gene encoding a toxic product. Gene, 136(1-2), 199-203. DOI
- Zeng, H., Yang, A. (2019) Quantification of proteomic and metabolic burdens predicts growth retardation and overflow metabolism in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 116(6):1484–95.
- Guleria, R., Jain, P., Verma, M., Mukherjee K.J. Designing next generation recombinant protein expression platforms by modulating the cellular stress response in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 19, 227 (2020). DOI
- Mahalik, S., Sharma, A. K., Jain, P., Mukherjee, K. J. (2017). Identifying genomic targets for protein over-expression by “omics” analysis of Quiescent Escherichia coli cultures. Microbial cell factories, 16 (1), 133. DOI
- Mahalik, S., Sharma, A., Das, D.R., Mittra, D., Mukherjee, K. J. (2022). Co-expressing leucine responsive regulatory protein (Lrp) enhances recombinant L-asparaginase-II production in Escherichia coli. Journal of biotechnology, 351, 99-108. DOI
- Sharma, A.K., Shukla, E., Janoti, D.S., Mukherjee, K.J., Shiloach, J. (2020) A novel knock out strategy to enhance recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Microbial cell factories, 19(1), 148. DOI
- Laxa, M. ( 2017) Intron-mediated enhancement: a tool for heterologous gene expression in plants? Frontiers in plant science, 7, 1977. DOI
- Georgiou, G., Valax, P. (1996) Expression of correctly folded proteins in Escherichia coli. Current opinion in biotechnology, 7(2), 190-197. DOI
- Andrews, B., Adari, H., Hannig, G., Lahue, E., Gosselin, M., Martin, S., Ahmed, A., Ford, P.J., Hayman, E.G., Makrides, S.C. (1996) A tightly regulated high level expression vector that utilizes a thermosensitive lac repressor: production of the human T cell receptor V beta 5.3 in Escherichia coli. Gene, 182(1-2), 101-109. DOI
- Freundlich, M., Ramani, N., Mathew, E., Sirko, A., Tsui, P. (1992) The role of integration host factor in gene expression in Escherichia coli. Molecular microbiology, 6(18), 2557-2563. DOI
- Giladi, H., Koby, S., Gottesman, M.E., Oppenheim, A.B. (1992) Supercoiling, integration host factor, and a dual promoter system, participate in the control of the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. Journal of molecular biology, 224(4), 937-948. DOI
- Harms, E., Wehner, A., Jennings, M.P., Pugh, K.J., Beacham, I.R., Rohm, K.H. (1991) Construction of expression systems for E. coli asparaginase II and two-step purification of the recombinant enzyme from periplasmic extracts. Protein expression and purification, 2, 144–150.
- Khushoo, A., Pal, Y., Singh, B.N., Mukherjee, K.J. (2004) Extracellular expression and single step purification of recombinant Escherichia coli L-asparaginase II. Protein expression and purification, 38(1), 29-36. DOI
- Galas, D.J., Eggert, M., Waterman, M.S. (1985) Rigorous patternrecognition methods for DNA sequences. Analysis of promoter sequences from Escherichia coli. Journal of molecular biology, 186(1), 117-128. DOI
- Du, F., Liu, Y.Q., Xu, Y.S., Fei, Du, Li, Z.J., Wang, Y.Z., Zhang, Z.X., Sun, X.M. (2021) Regulating the T7 RNA polymerase expression in E. coli BL21 (DE3) to provide more host options for recombinant protein production. Microbial cell factories, 20, 189. DOI
- Lisser, S., Margalit, H. (1993). Compilation of E. coli mRNA promoter sequences. Nucleic acids research, 21(7), 1507–1516. DOI
- Chohan, S.M., Rashid, N. (2013) TK1656, a thermostable L-asparaginase from Thermococcus kodakaraensis, exhibiting highest ever reported enzyme activity. Journal of bioscience and bioengineering, 116(4), 438-443. DOI
- Remaut, E., Tsao, H., Fiers, W. (1983) Improved plasmid vectors with a thermoinducible expression and temperature-regulated runaway replication. Gene, 22(1), 103-113. DOI
- Yang, J., Ruff, A. J., Hamer, S. N., Cheng, F., Schwaneberg, U. (2016). Screening through the PLICable promoter toolbox enhances protein production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology journal, 11(12), 1639-1647. DOI
- Mohammadzadeh, R., Karbalaei, M., Soleimanpour, S., Mosavat, A., Rezaee, S.A., Ghazvini, K., Farsiani, H. (2021) Practical methods for expression of recombinant protein in the Pichia pastoris system. Current protocols, 1(6), e155. DOI
- Vogl, T. (2022) Engineering of promoters for gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Methods in molecular biology, 2513, 153-177. DOI
- Yang, J., Cai, H., Liu, J., Zeng, M., Chen, J., Cheng, Q., Zhang, L. (2018) Controlling AOX1 promoter strength in Pichia pastoris by manipulating poly (dA:dT) tracts. Scientific reports, 8(1), 1401. DOI
- Özçelik, A., Yılmaz, S., Inan, M. (2019) Pichia pastoris Promoters. Methods in molecular biology, 1923, 97-112. DOI
- Effer, B., Lima, G.M., Cabarca, S., Pessoa, A., Farías, J.G., Monteiro, G. (2019) L-asparaginase from E. chrysanthemi expressed in Glycoswitch®: effect of His-Tag fusion on the extracellular expression. Preparative biochemistry & biotechnology, 49(7), 679-685. DOI
- Vogl, T., Kickenweiz, T., Pitzer, J., Sturmberger, L., Weninger, A., Biggs, B.W., Köhler, E.M., Baumschlager, A., Fischer, J.E., Hyden, P., Wagner, M., Baumann, M., Borth, N., Geier, M., Ajikumar, P.K., Glieder, A. (2018) Engineered bidirectional promoters enable rapid multi-gene co-expression optimization. Nature communications, 9(1), 3589. DOI
- Tien Cuong, Nguyen, Nguyen, Trang, Tuyen, Do, Thi, Quyen, D.T. (2014). Expression, purification and evaluation of recombinant L-asparaginase in mehthylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Journal of Vietnamese Environment 6(3):288-292 DOI
- Yang, S., Du, G., Chen, J., Kang, Z. (2017) Characterization and application of endogenous phase-dependent promoters in Bacillus subtilis. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 101(10), 4151-4161. DOI
- Niu, J., Yan, R., Shen, J., Zhu, X., Meng, F., Lu, Z., Lu, F. (2022). Cis-element engineering promotes the expression of Bacillus subtilis type I L-asparaginase and its application in food. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (12), 6588. DOI
- Rao, Y., Cai, D., Wang, H., Xu, Y., Xiong, S., Gao, L., Xiong, M., Wang, Z., Chen, S., Ma, X. (2020) Construction and application of a dual promoter system for efficient protein production and metabolic pathway enhancement in Bacillus licheniformis. Journal of biotechnology, 312, 1-10. DOI
- Zhao, X., Xu, J., Tan, M., Zhen, J., Shu, W., Yang, S., Ma, Y., Zheng, H., Song, H. (2020) High copy number and highly stable Escherichia coli-Bacillus subtilis shuttle plasmids based on pWB980. Microbial Cell Factories, 19(1), 25. DOI
- Schumann, W. (2007) Production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Advances in applied microbiology, 2, 137-189. DOI
- Erden-Karaoğlan, F., Karaoğlan, M. (2023) Improvement of recombinant L-asparaginase production in Pichia pastoris. 3 Biotech, 13(5), 164. DOI
- McCarthy, J.E., Brimacombe, R. (1994) Prokaryotic translation: the interactive pathway leading to initiation. Trends in genetics, 10(11), 402-407. DOI
- Ringquist, S., Shinedling, S., Barrick, D., Green, L., Binkley, J., Stormo, G.D., Gold, L. (1992) Translation initiation in Escherichia coli: sequences within the ribosome-binding site. Molecular microbiology, 6(9), 1219-1229. DOI
- Kozak, M. (1999) Initiation of translation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene, 234(2), 187-208. DOI
- de Smit, M.H., van Duin, J. (1994) Control of translation by mRNA secondary structure in Escherichia coli. A quantitative analysis of literature data. Journal of molecular biology, 244(2), 144-150. DOI
- Shine, J., Dalgarno, L. (1974) The 3’-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 71(4), 1342-1346. DOI
- Hüttenhofer, A., Noller, H.F. (1994) Footprinting mRNA-ribosome complexes with chemical probes. The EMBO journal, 13(16), 3892-3901. DOI
- Scherer, G.F., Walkinshaw, M.D., Arnott, S., Morré, D.J. (1980) The ribosome binding sites recognized by E. coli ribosomes have regions with signal character in both the leader and protein coding segments. Nucleic acids research, 8(17), 3895-3907. DOI
- Chen, H., Bjerknes, M., Kumar, R., Jay, E. (1994) Determination of the optimal aligned spacing between the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and the translation initiation codon of Escherichia coli mRNAs. Nucleic acids research, 22(23), 4953-4957. DOI
- Chen, H., Pomeroy-Cloney, L., Bjerknes, M., Tam, J., Jay, E. (1994) The influence of adenine-rich motifs in the 3’ portion of the ribosome binding site on human IFN-gamma gene expression in Escherichia coli. Journal of molecular biology, 240(1), 20-27. DOI
- Wilson, B.S., Kautzer, C.R., Antelman, D.E. (1994) Increased protein expression through improved ribosome-binding sites obtained by library mutagenesis. Biotechniques, 17(5), 944-953.
- Nishi, T., Itoh, S. (1986) Enhancement of transcriptional activity of the Escherichia coli trp promoter by upstream A + T-rich regions. Gene, 44(1), 29- 36. DOI
- Stanssens, P., Remaut, E., Fiers, W. (1985) Alterations upstream from the Shine-Dalgarno region and their effect on bacterial gene expression. Gene, 36(3), 211-223. DOI
- Warburton, N., Boseley, P.G., Porter, A.G. (1983) Increased expression of a cloned gene by local mutagenesis of its promoter and ribosome binding site. Nucleic acids research, 11(17), 5837-5854. DOI
- Salis, H.M., Mirsky, E.A., Voigt, C.A. (2009) Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression. Nature biotechnology, 27(10), 946-950. DOI
- Zhu, M., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Lin, W., Xu, M., Yang, T., Shao, M., Rao, Z. (2021) Molecular modification and highly efficient expression of L-asparaginase from Rhizomucor miehei. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 37(9), 3242-3252. DOI
- Stormo, G.D., Schneider, T.D., Gold, L.M. (1982) Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic acids research, 10(9), 2971-2996. DOI
- Sprengart, M.L., Fuchs, E., Porter, A.G. (1996) The downstream box: an efficient and independent translation initiation signal in Escherichia coli. The EMBO journal, 15(3), 665-674
- de Smit, M.H., van Duin, J. (1990) Secondary structure of the ribosome binding site determines translational efficiency: a quantitative analysis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 87(19), 7668-7672. DOI
- Hall, M.N., Gabay, J., Débarbouillé, M., Schwartz, M. (1982) A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature, 295(5850), 616-618. DOI
- Wikström, P.M., Lind, L.K., Berg, D.E., Björk, G.R. (1992) Importance of mRNA folding and start codon accessibility in the expression of genes in a ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli. Journal of molecular biology, 224(4), 949-966. DOI
- Gross, G., Mielke, C., Hollatz, I., Blöcker, H., Frank, R. (1990) RNA primary sequence or secondary structure in the translational initiation region controls expression of two variant interferon-beta genes in Escherichia coli. The Journal of biological chemistry, 265(29), 17627-17636. DOI
- Ramesh, V., De, A., Nagaraja, V. (1994) Engineering hyperexpression of bacteriophage Mu C protein by removal of secondary structure at the translation initiation region. Protein engineering, 7(8), 1053-1057. DOI
- Nora, L.C., Westmann, C.A., Martins-Santana, L., Alves, L.F., Monteiro, L.M.O., Guazzaroni, M.E., Silva-Rocha, R. (2019) The art of vector engineering: towards the construction of next-generation genetic tools. Microbial biotechnology, 12(1), 125-147. DOI
- Rosenberg, M., Court, D. (1979) Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annual review of genetics, 13, 319-353. DOI
- Sharp, P.M., Bulmer, M. (1988) Selective differences among translation termination codons. Gene, 63(1), 141-145. DOI
- Poole, E.S., Brown, C.M., Tate, W.P. (1995) The identity of the base following the stop codon determines the efficiency of in vivo translational termination in Escherichia coli. The EMBO journal, 14(1), 151-158. DOI
- Tate, W.P., Brown, C.M. (1992) Translational termination: “stop” for protein synthesis or “pause” for regulation of gene expression. Biochemistry, 31(9), 2443-2450. DOI
- Chamberlin, M.J. (1992) New models for the mechanism of transcription elongation and its regulation. Harvey lectures, 88:1-21.
- Platt, T. ( 1986) Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annual review of biochemistry, 55, 339-372. DOI
- Richardson, J.P. (1993) Transcription termination. Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology, 28(1), 1-30. DOI
- Richardson J.P, Greenblatt J.L. (1996) Control of RNA chain elongation and termination. In Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology (Neidhardt, F.ed.) Washington, DC, pp. 822-848
- Jensen, K., Bonekamp, F., Scharff-Poulsen, Peter. (1986) Attenuation at nucleotide biosynthetic genes and amino acid biosynthetic operons of Escherichia coli. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 11(9), 362-365. DOI
- Qayyum, M.Z., Dey, D., Sen, R. (2016) Transcription Elongation Factor NusA Is a General Antagonist of Rho-dependent Termination in Escherichia coli.The Journal of biological chemistry, 291(15), 8090-8108. DOI
- Brosius, J., Ullrich, A., Raker, M.A., Gray, A., Dull, T.J., Gutell, R.R., Noller, H.F. (1981) Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid, 6(1), 112-118. DOI
- Condon, C., Squires, C., Squires, C.L. (1995) Control of rRNA transcription in Escherichia coli. Microbiological reviews, 59(4), 623-645. DOI
- Kane, J.F. (1995) Effects of rare codon clusters on high-level expression of heterologous proteins in Escherichia coli. Current opinion in biotechnology, 6(5), 494-500. DOI
- Zhang, S.P., Zubay, G., Goldman, E. (1991) Low-usage codons in Escherichia coli, yeast, fruit fly and primates. Gene, 105(1), 61-72. DOI
- Xu, Y., Liu, K., Han, Y., Xing, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, Q., Zhou, M. (2021) Codon usage bias regulates gene expression and protein conformation in yeast expression system P. pastoris. Microbial Cell Factories, 20(1), 91. DOI
- Gouy, M., Gautier, C. (1982) Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic acids research, 10(22), 7055-7074. DOI
- Dana, A., Tuller, T. (2014) The effect of tRNA levels on decoding times of mRNA codons. Nucleic acids research, 42(14), 9171-9181. DOI
- Sharp, P.M., Cowe, E., Higgins, D.G., Shields, D.C., Wolfe, K.H., Wright, F. (1988) Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable withinspecies diversity. Nucleic acids research, 16(17), 8207-8211. DOI
- Yu, C.H., Dang, Y., Zhou, Z., Wu, C., Zhao, F., Sachs, M.S., Liu, Y. (2015) Codon usage influences the local rate of translation elongation to regulate cotranslational protein folding. Molecular cell, 59(5), 744-754. DOI
- Singha, T. K., Gulati, P., Mohanty, A., Khasa, Y. P., Kapoor, R. K., Kumar, S. (2017). Efficient genetic approaches for improvement of plasmid based expression of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli: A review. Process Biochemistry, 55, 17-31. DOI
- Chen, G.T., Inouye, M. (1994) Role of the AGA/AGG codons, the rarest codons in global gene expression in Escherichia coli. Genes & development, 8(21), 2641-2652. DOI
- Chen, K.S., Peters, T.C., Walker, J.R. (1990) A minor arginine tRNA mutant limits translation preferentially of a protein dependent on the cognate codon. Journal of bacteriology, 172(5), 2504-2510. DOI
- Hernan, R.A., Hui, H.L., Andracki, M.E., Noble, R.W., Sligar, S.G., Walder, J.A., Walder, R.Y. (1992) Human hemoglobin expression in Escherichia coli: importance of optimal codon usage. Biochemistry, 31(36), 8619-8628. DOI
- Ernst, J. F., Kawashima, E. (1988) Variations in codon usage are not correlated with heterologous gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Journal of biotechnology, 7(1), 1-9. DOI
- Lee, H.W., Joo, J.H., Kang, S.S., Song, J.B., Kwon, M.H., Han, D.S., Na, D.S. (1992) Expression of human interleukin-2 from native and synthetic genes in E. coli: No correlation between major codon bias and high level expression. Biotechnology Letters, 14, 653-658. DOI
- Gustafsson, C., Govindarajan, S., Minshull, J. (2004) Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends in biotechnology, 22(7), 346-353. DOI
- Komar, A.A. (2016). The art of gene redesign and recombinant protein production: approaches and perspectives. In proteint herapeutics. Topics in medicinal chemistry (Sauna, Z., Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. eds) Springer, Cham. 21 pp161-177. DOI
- Wu, G., Zheng, Y., Qureshi, I., Zin, H.T., Beck, T., Bulka, B., Freeland, S.J. (2006) SGDB: a database of synthetic genes re-designed for optimizing protein over-expression. Nucleic acids research, 35, D76-D79. DOI
- Einsfeldt, K., Baptista, I.C., Pereira, J.C., Costa-Amaral, I.C., Costa, E.S., Ribeiro, M.C., Land, M.G., Alves, T.L., Larentis, A.L., Almeida, R.V. (2016) Recombinant L-asparaginase from Zymomonas mobilis: A potential new antileukemic agent produced in Escherichia coli. PLoS One., 11(6), e0156692. DOI
- Kimchi-Sarfaty, C., Oh, J.M., Kim, I.W., Sauna, Z.E., Calcagno, A.M., Ambudkar, S.V., Gottesman, M.M. (2007) A “silent” polymorphism in the MDR1 gene changes substrate specificity. Science, 315(5811), 525-528. DOI
- Komar, A.A. (2009) A pause for thought along the co-translational folding pathway. Trends in biochemical sciences, 34(1), 16-24. DOI
- Kim, S.J., Yoon, J.S., Shishido, H., Yang, Z., Rooney, L.A., Barral, J.M., Skach, W.R. (2015) Protein folding. Translational tuning optimizes nascent protein folding in cells. Science, 348(6233), 444-448. DOI
- Buhr, F., Jha, S., Thommen, M., Mittelstaet, J., Kutz, F., Schwalbe, H., Rodnina, M.V., Komar, A.A. (2016) Synonymous Codons Direct Cotranslational Folding toward Different Protein Conformations. Molecular cell, 61(3), 341- 351. DOI
- Goldman, E., Rosenberg, A.H., Zubay, G., Studier, F.W. (1995) Consecutive low-usage leucine codons block translation only when near the 5’ end of a message in Escherichia coli. Journal of molecular biology, 245(5), 467-473. DOI
- Bulmer, M. (1988) Codon usage and intragenic position. Journal of theoretical biology, 133(1), 67-71. DOI
- Chen, G.F., Inouye, T.M. (1990) Suppression of the negative effect of minor arginine codons on gene expression; preferential usage of minor codons within the first 25 codons of the Escherichia coli genes. Nucleic acids research, 18(6), 1465-1473. DOI
- Boer, H.A., Kastelein, R.A. (1986) Biased codon usage: an exploration of its role in optimization of translation. In Biotechnology Series. pp. 225-285.
- Eyre-Walker, A., Bulmer, M. (1993) Reduced synonymous substitution rate at the start of enterobacterial genes. Nucleic acids research, 21(19), 4599-4603. DOI
- Irwin, B., Heck, J.D., Hatfield, G.W. (1995) Codon pair utilization biases influence translational elongation step times. The Journal of biological chemistry, 270(39), 22801-22806. DOI
- Rosenberg, A.H., Goldman, E., Dunn, J.J., Studier, F.W., Zubay, G. (1993) Effects of consecutive AGG codons on translation in Escherichia coli, demonstrated with a versatile codon test system. Journal of bacteriology, 175(3), 716-722. DOI
- Saier, M.H. Jr. (1995) Differential codon usage: a safeguard against inappropriate expression of specialized genes? FEBS letters, 362(1), 1-4. DOI
- Mortazavi, M., Torkzadeh-Mahani, M., Kargar, F., Nezafat N., Younes G. (2019) In silico analysis of codon usage and rare codon clusters in the halophilic bacteria L-asparaginase. Biologia, 75(4), 151-160. DOI
- Hatfield, G.W., Hung, S.P., Baldi, P. (2003) Differential analysis of DNA microarray gene expression data. Molecular microbiology, 47(4), 871-877. DOI
- Trapnell, C., Roberts, A., Goff, L., Pertea, G., Kim, D., Kelley, D.R., Pimentel, H., Salzberg, S.L., Rinn, J.L., Pachter, L. (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nature protocols, 7(3), 562-578. DOI
- Ghosh, D., Chinnaiyan, A.M. (2002) Mixture modelling of gene expression data from microarray experiments. Bioinformatics, 18(2), 275-886. DOI
- Kerr, M.K., Churchill, G.A. (2001) Statistical design and the analysis of gene expression microarray data. Genet Res. 77(2), 123-128. DOI
- Mollah, M.M., Jamal, R., Mokhtar, N.M., Harun, R., Mollah, M.N. (2015) A Hybrid one-way ANOVA approach for the robust and efficient estimation of differential gene expression with multiple patterns. PLoS one, 10(9), e0138810. DOI
- Tarazona, S., Furió-Tarí, P., Turrà, D., Pietro, A.D., Nueda, M.J., Ferrer, A., Conesa, A. (2015) Data quality aware analysis of differential expression in RNA-seq with NOISeq R/Bioc package. Nucleic acids research, 43(21), e140. DOI
- Ross, J. (1995) mRNA stability in mammalian cells. Microbiological reviews, 59(3), 423-450. DOI
- Brenner, S., Jacob, F., Meselson, M. (1961) An unstable intermediate carrying information from genes to ribosomes for protein synthesis. Nature, 190, 576-581. DOI
- Ehretsmann, C.P., Carpousis, A.J., Krisch, H.M. (1992) mRNA degradation in procaryotes. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 6(13), 3186-3192. DOI
- Mugridge, J.S., Coller, J., Gross, J.D. (2018) Structural and molecular mechanisms for the control of eukaryotic 5’-3’ mRNA decay. Nature structural & molecular biology, 25(12), 1077-1085. DOI
- Nierlich, D.P., Murakawa, G.J. (1996) The decay of bacterial messenger RNA. Progress in nucleic acid research and molecular biology, 52, 153-216. DOI
- Petersen, C. (1992) Control of functional mRNA stability in bacteria: multiple mechanisms of nucleolytic and non-nucleolytic inactivation. Molecular microbiology, 6(3), 277-282. DOI
- Donovan, W.P., Kushner, S.R. (1986) Polynucleotide phosphorylase and ribonuclease II are required for cell viability and mRNA turnover in Escherichia coli K-12. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 83(1), 120-124. DOI
- Har-El, R., Silberstein, A., Kuhn, J., Tal, M. (1979) Synthesis and degradation of lac mRNA in E. coli depleted of 30S ribosomal subunits. Molecular & general genetics, 173(2), 135-144. DOI
- Merino, E., Becerril, B., Valle, F., Bolivar, F. (1987) Deletion of a repetitive extragenic palindromic (REP) sequence downstream from the structural gene of Escherichia coli glutamate dehydrogenase affects the stability of its mRNA. Gene, 58(2-3), 305-309. DOI
- Newbury, S.F., Smith, N.H., Robinson, E.C., Hiles, I.D., Higgins, C.F. (1987) Stabilization of translationally active mRNA by prokaryotic REP sequences. Cell, 48(2), 297-310. DOI
- Chen, L.H., Emory, S.A., Bricker, A.L., Bouvet, P., Belasco, J.G. (1991) Structure and function of a bacterial mRNA stabilizer: analysis of the 5’ untranslated region of ompA mRNA. Journal of bacteriology, 173(15), 4578- 4586. DOI
- Emory, S.A., Belasco, J.G. (1990) The ompA 5’ untranslated RNA segment functions in Escherichia coli as a growth-rate-regulated mRNA stabilizer whose activity is unrelated to translational efficiency. Journal of bacteriology, 172(8), 4472-4481. DOI
- Alifano, P., Bruni, C.B., Carlomagno, M.S. (1994) Control of mRNA processing and decay in prokaryotes. Genetica, 94(2-3), 157-172. DOI
- Nilsson, G., Belasco, J.G., Cohen, S.N., von Gabain, A. (1984) Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature, 312(5989), 75-77. DOI
- Mohanty, B. K., Kushner, S. R. (2003). Genomic analysis in Escherichia coli demonstrates differential roles for polynucleotide phosphorylase and RNase II in mRNA abundance and decay. Molecular microbiology, 50(2), 645–658. DOI
- Fontes, A. M., Ito, J., Jacobs-Lorena, M. (1999). Control of messenger RNA stability during development. Current topics in developmental biology, 44, 171–202. DOI
- Duvoisin, R.M., Belin, D., Krisch, H.M. (1986) A plasmid expression vector that permits stabilization of both mRNAs and proteins encoded by the cloned genes. Gene, 45(2), 193-201. DOI
- Gorski, K., Roch, J.M., Prentki, P., Krisch, H.M. (1985) The stability of bacteriophage T4 gene 32 mRNA: a 5’ leader sequence that can stabilize mRNA transcripts. Cell, 43(2 Pt 1), 461-469. DOI
- Bandyra, K., Luisi, B. (2013). mRNA Degradation in Prokaryotes. In Encyclopedia of Biophysics.(Roberts, G.C.K. ed.) Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. pp.1605-1611. DOI
- Wong, H.C., Chang, S. (1986) Identification of a positive retroregulator that stabilizes mRNAs in bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 83(10), 3233-3237. OI: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3233
- Belasco, J.G., Nilsson, G., von Gabain, A., Cohen, S.N. (1986) The stability of E. coli gene transcripts is dependent on determinants localized to specific mRNA segments. Cell, 46(2), 245-251. DOI
- Belasco, J.G., Higgins, C.F. (1988) Mechanisms of mRNA decay in bacteria: a perspective. Gene, 72(1-2), 15-23. DOI
- Chen, C.Y., Beatty, J.T., Cohen, S.N., Belasco, J.G. (1988) An intercistronic stem-loop structure functions as an mRNA decay terminator necessary but insufficient for puf mRNA stability. Cell, 52(4), 609-619. DOI
- Guarneros, G., Montañez, C., Hernandez, T., Court, D. (1982) Posttranscriptional control of bacteriophage lambda gene expression from a site distal to the gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 79(2), 238-242. DOI
- Higgins, C.F., Causton, H.C., Dance, G.S.C., Mudd, E.A. (1993) The role of the 3′ end in mRNA stability and decay. In Control of Messenger RNA Stability ( J. Belasco, G. Brawerman Eds.) Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp. 13-30. DOI
- Carzaniga, T., Sbarufatti, G., Briani, F. Gianni Dehò G. (2017). Polynucleotide phosphorylase is implicated in homologous recombination and DNA repair in Escherichia coli . BMC Microbiol 17 (81). DOI
- Goldberg, A.L., Goff, S.A. (1986) The selective degradation of abnormal proteins in bacteria. In Maximizing gene expression (W.Reznikoff , L.Gold eds) Butterworths, Boston, pp 287-314.
- Gottesman, S. (1990) Minimizing proteolysis in Escherichia coli: genetic solutions. Methods in enzymology, 185, 119-129. DOI
- Miller, C. G. 1996. Protein degradation and proteolytic modification, In Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology.(F.C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E.C.C. Lin, K.B. Low, B. Magasanik, W.S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter, H. E. Umbarger ed.), ASM Press, Washington, D.C. p. 938-954.
- Baneyx, F., Georgiou, G. (1992) Degradation of secreted proteins in Escherichia coli. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 665, 301-308. DOI
- Kaufmann, A., Stierhof, Y.D., Henning, U. (1994) New outer membraneassociated protease of Escherichia coli K-12. Journal of bacteriology, 176(2), 359-367. DOI
- Keiler, K.C., Waller, P.R., Sauer, R.T. (1996) Role of a peptide tagging system in degradation of proteins synthesized from damaged messenger RNA. Science, 271(5251), 990-993. DOI
- Baneyx, F., Georgiou, G. (1991) Construction and characterization of Escherichia coli strains deficient in multiple secreted proteases: protease III degrades high-molecular-weight substrates in vivo. Journal of bacteriology, 173(8), 2696-2703. DOI
- Baneyx, F., G. Georgiou. 1992 Expression of proteolytically sensitive polypeptides in Escherichia coli, In stability of protein pharmaceuticals. A.chemical and physical pathways of protein degradation. (T.J. Ahern and M.C. Manning (ed.) Plenum Press, New York.pp. 69-108.
- Murby, M., Uhlén, M., Ståhl, S. (1996) Upstream strategies to minimize proteolytic degradation upon recombinant production in Escherichia coli. Protein expression and purification, 7(2), 129-136. DOI
- Bachmair, A., Finley, D., Varshavsky, A. (1986) In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science, 234(4773), 179-186. DOI
- Bachmair, A., Varshavsky, A. (1989) The degradation signal in a short-lived protein. Cell, 56(6), 1019-1032. DOI
- Gonda, D.K., Bachmair, A., Wünning, I., Tobias, J.W., Lane, W.S., Varshavsky, A. (1989) Universality and structure of the N-end rule. The Journal of biological chemistry, 264(28), 16700-16712. DOI
- Tobias, J.W., Shrader, T.E., Rocap, G., Varshavsky, A. (1991) The N-end rule in bacteria. Science, 254(5036), 1374-1337. DOI
- Varshavsky, A. (1992) The N-end rule. Cell, 69(5), 725-735. DOI
- Rogers, S., Wells, R., Rechsteiner, M. (1990) Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science, 234(4774), 364-368. DOI
- Murby, M., Samuelsson, E., Nguyen, T.N., Mignard, L., Power, U., Binz, H., Uhlén, M., Ståhl, S. (1995) Hydrophobicity engineering to increase solubility and stability of a recombinant protein from respiratory syncytial virus. European journal of biochemistry, 230(1), 38-44. DOI
- Hammarberg, B., Nygren, P.A., Holmgren, E., Elmblad, A., Tally, M., Hellman, U., Moks, T., Uhlén, M. (1989) Dual affinity fusion approach and its use to express recombinant human insulin-like growth factor II. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 86(12), 4367- 4371. DOI
- Hellebust, H., Murby, M., Abrahmsén, L, Uhle´n M., Enfors S.-O. (1989) Different approaches to stabilize a recombinant fusion protein. Nature biotechnology, 7, 165-168. DOI
- Carter, P. (1990) Site-specific proteolysis of fusion proteins. In: Protein Purification: From Molecular Mechanism to Large-Scale Processes. (R. Ladisch, R.C. Willson, C.C. Painton, S.E. Builder (Eds.). Symposium Series, 427, American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C. pp. 181-193.
- Forsberg, G., Baastrup, B., Rondahl, H., Holmgren, E., Pohl, G., Hartmanis, M., Lake, M. (1992) An evaluation of different enzymatic cleavage methods for recombinant fusion proteins, applied on des(1-3)insulin-like growth factor I. Journal of protein chemistry, 11(2), 201-211. DOI
- Nilsson, B., Forsberg, G., Moks, T., Hartmanis, M., Uhlén, M. (1992). Fusion proteins in biotechnology and structural biology. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2(4), 569-575. DOI
- Nygren, P.A., Ståhl, S., Uhlén, M. (1994) Engineering proteins to facilitate bioprocessing. Trends in biotechnology, 12(5), 184-188. DOI
- Uhlén, M., Moks, T. (1990) Gene fusions for purpose of expression: an introduction. Methods in enzymology, 185, 129-143. DOI
- Shen, S.H. (1984) Multiple joined genes prevent product degradation in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America, 81(15), 4627-4631. DOI
- Bowie, J.U., Sauer, R.T. (1989) Identification of C-terminal extensions that protect proteins from intracellular proteolysis.The Journal of biological chemistry, 264(13), 7596-7602
- Koken, M.H., Odijk, H.H., van Duin, M., Fornerod, M., Hoeijmakers, J.H. (1993) Augmentation of protein production by a combination of the T7 RNA polymerase system and ubiquitin fusion: overproduction of the human DNA repair protein, ERCC1, as a ubiquitin fusion protein in Escherichia coli. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 195(2), 643-653. DOI
- Blondel, A., Nageotte, R., Bedouelle, H. (1996) Destabilizing interactions between the partners of a bifunctional fusion protein. Protein engineering, 9(2), 2312-2318. DOI
- Patel, N., Krishnan, S., Offman, M.N., Krol, M., Moss, C.X., Leighton, C., van Delft, F.W., Holland, M., Liu, J., Alexander, S., Dempsey, С., Ariffin, H., Essink, M., Eden, T.O.B., Watts, C., Bates, P.A., Saha, V.(2009) A dyad of lymphoblastic lysosomal cysteine proteases degrades the antileukemic drug L-asparaginase. Journal of Clinical. Investigation, 119 (7), 1964–1973. DOI
- Obukowicz, M.G., Staten, N.R., Krivi, G.G. (1992) Enhanced heterologous gene expression in novel rpoH mutants of Escherichia coli. Applied and environmental microbiology, 58(5), 1511-1523. DOI
- Goldberg, A.L., Goff S.A., Casson L.P. (1988). Hosts and methods for producing recombinant products in high yields.WIPO (PCT) U.S. WO1985003949A1
- Meerman, H.J., Georgiou, G. (1994) High-level production of proteolytically sensitive secreted proteins in Escherichia coli strains impaired in the heat-shock response. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 21, 292-302. DOI
- Spiess, C., Beil, A., Ehrmann, M. (1999) A temperature-dependent switch from chaperone to protease in a widely conserved heat shock protein. Cell, 97(3), 339-347. DOI
- Rizzitello, A.E, Harper, J.R., Silhavy, T.J. (2001) Genetic evidence for parallel pathways of chaperone activity in the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Journal of bacteriology, 183(23), 6794-6800. DOI
- Safder, I., Khan, S., Islam, I., Ali MK, Bibi Z, Waqas M. (2018) Pichia pastoris Expression system: A potential candidate to express protein inindustrial and biopharmaceutical domains. Biomedical letters, 4(1), 1-14, DOI
- Hamed, M.B., Anné, J., Karamanou, S., Economou, A. (2018). Streptomyces protein secretion and its application in biotechnology. FEMS microbiology letters, 365(22), fny250. DOI
- Radha, R., Arumugam, N., Gummadi, S.N. (2018) Glutaminase free L-asparaginase from Vibrio cholerae: Heterologous expression, purification and biochemical characterization. International journal of biological macromolecules, 111, 129-138. DOI
- Coleman, R.J., Bruck, T. ( 2020) Method for production of recombinant erwinia asparaginase. US Patent No: 10,787,671 B2 Sep. 29
- Simon, L.D., Randolph, B., Irwin, N., Binkowski, G. (1983) Stabilization of proteins by a bacteriophage T4 gene cloned in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of america, 80(7), 2059- 2062. DOI
- Singer, B.S., Gold, L. (1991) Phage T4 expression vector: protection from proteolysis. Gene, 106(1), 1-6. DOI
- Lee, S.Y. (1996) High cell-density culture of Escherichia coli. Trends in biotechnology, 14(3), 98-105. DOI
- Swamy, K.H., Goldberg, A.L. (1982) Subcellular distribution of various proteases in Escherichia coli. Journal of bacteriology, 149(3), 1027-1033. DOI
- Talmadge, K., Gilbert, W. (1982) Cellular location affects protein stability in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the united states of America, 79(6), 1830-1833. DOI
- Fahey, R.C., Hunt, J.S., Windham, G.C. (1977) On the cysteine and cystine content of proteins. Differences between intracellular and extracellular proteins. Journal of molecular evolution, 10(2), 155-160. DOI
- Hwang, C., Sinskey, A.J., Lodish, H.F. (1992) Oxidized redox state of glutathione in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science, 257(5076), 1496-1502. DOI
- Bardwell, J.C. (1994) Building bridges: disulphide bond formation in the cell. Molecular microbiology, 14(2), 199-205. DOI
- Bardwell, J.C., McGovern, K., Beckwith, J. (1991) Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell, 67(3), 581-589. DOI
- Guilhot, C., Jander, G., Martin, N.L., Beckwith, J. (1995) Evidence that the pathway of disulfide bond formation in Escherichia coli involves interactions between the cysteines of DsbB and DsbA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92(21), 9895-9899. DOI
- Pugsley, A.P. (1993) The complete general secretory pathway in gramnegative bacteria. Microbiological reviews, 57(1), 50-108. DOI
- Stader, J.A., Silhavy, T.J. (1990) Engineering Escherichia coli to secrete heterologous gene products. Methods in enzymology, 185, 166-187. DOI
- Petrovskaia, L.E., Ruzin, A.V., Shingarova, L.N., Korobko, V.G. (1995) Design of recombinant Escherichia coli strains, determining the secretory expression of artificial human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor genes. Bioorganicheskaia khimiia, 21(11), 845-854.
- Georgiou, G., Segatori, L. (2005) Preparative expression of secreted proteins in bacteria: status report and future prospects. Current opinion in biotechnology, 16(5), 538-545. DOI
- Hodgson, J. (1993) Expression systems: a user’s guide. Emphasis has shifted from the vector construct to the host organism. Biotechnology (N Y), 11(8), 887-893. DOI
- Blight, M.A., Chervaux, C., Holland, I.B. (1994) Protein secretion pathway in Escherichia coli. Current opinion in biotechnology, 5(5), 468-474. DOI
- Saier, M.H. Jr, Werner. P.K., Müller, M. (1989) Insertion of proteins into bacterial membranes: mechanism, characteristics, and comparisons with the eucaryotic process. Microbiological reviews, 53(3), 333-366. DOI
- Pérez-Pérez, J., Márquez, G., Barbero, J.L, Gutiérrez, J. (1994) Increasing the efficiency of protein export in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology (N Y), 12(2), 178-180. DOI
- Schatz, P.J., Beckwith, J. (1990) Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annual review of genetics, 24, 215-248. DOI
- Schatz, G., Dobberstein, B. (1996) Common principles of protein translocation across membranes. Science, 271(5255), 1519-1526. DOI
- von Heijne, G. (1990) The signal peptide. The Journal of membrane biology, 115(3), 195-201. DOI
- Kern, I., Cegłowski, P. (1995) Secretion of streptokinase fusion proteins from Escherichia coli cells through the hemolysin transporter. Gene, 163(1), 53-57. DOI
- Hoffman, C.S., Wright, A. (1985) Fusions of secreted proteins to alkaline phosphatase: an approach for studying protein secretion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 82(15), 5107- 5111. DOI
- Kadonaga, J.T., Gautier, A.E., Straus, D.R., Charles, A.D., Edge, M.D., Knowles, J.R. (1984) The role of the beta-lactamase signal sequence in the secretion of proteins by Escherichia coli. The Journal of biological chemistry, 259(4), 2149-2154. DOI
- Morioka-Fujimoto, K., Marumoto, R., Fukuda, T. (1991) Modified enterotoxin signal sequences increase secretion level of the recombinant human epidermal growth factor in Escherichia coli.The Journal of biological chemistry, 266(3), 1728-1732
- Abrahmsén, L., Moks, T., Nilsson, B., Uhlén, M. (1986) Secretion of heterologous gene products to the culture medium of Escherichia coli. Nucleic acids research, 14(18), 7487-7500. DOI
- Lo, A.C., MacKay, R.M., Seligy, V.L., Willick, G.E. (1988) Bacillus subtilis beta-1,4-endoglucanase products from intact and truncated genes are secreted into the extracellular medium by Escherichia coli. Applied and environmental microbiology, 54(9), 2287-2292. DOI
- Le Calvez, H., Green, J.M., Baty, D. (1996) Increased efficiency of alkaline phosphatase production levels in Escherichia coli using a degenerate PelB signal sequence. Gene, 170(1), 51-55. DOI
- Schein, C.H., Boix, E., Haugg, M., Holliger, K.P., Hemmi, S., Frank, G., Schwalbe, H. (1992) Secretion of mammalian ribonucleases from Escherichia coli using the signal sequence of murine spleen ribonuclease. The Biochemical journal, 283 ( Pt 1), 137-144. DOI
- Yari, M., Ghoshoon, M.B., Nezafat, N., Younes, G. (2020) Experimental evaluation of in silico selected signal peptides for secretory expression of Erwinia asparaginase in Escherichia coli. International journal of peptide research and therapeutics, 26, 1583-1591. DOI
- Chan, W.K., Lorenzi, P.L., Anishkin, A., Purwaha, P., Rogers, D.M., Sukharev, S., Rempe, S.B., Weinstein, J.N. (2014) The glutaminase activity of L-asparaginase is not required for anticancer activity against ASNS-negative cells. Blood, 123(23), 3596-3606. DOI
- Obukowicz, M.G., Turner, M.A., Wong, E.Y., Tacon, W.C. (1988) Secretion and export of IGF-1 in Escherichia coli strain JM101. Molecular & general genetics, 215(1), 19-25. DOI
- Hsiung, H., Cantrell, A., Luirink, J. B. Oudega, B., Veros, A. J., Becker,G. W. (1989) Use of bacteriocin release protein in E. Coli for excretion of human growth hormone into the culture medium. Nature biotechnology, 7, 267-271. DOI
- Aristidou, A.A., Yu, P., San, K.Y. (1993) Effects of glycine supplement on protein production and release in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnology Letters, 15, 331-336. DOI
- Kobayashi, T., Kato, C., Kudo, T., Horikoshi, K. (1986) Excretion of the penicillinase of an alkalophilic Bacillus sp. through the Escherichia coli outer membrane is caused by insertional activation of the kil gene in plasmid pMB9. Journal of bacteriology, 166(3), 728-732. DOI
- Yu, P., Aristidou, A.A., San, K.Y. (1991) Synergistic effect of glycine and bacteriocin release protein in the release of periplasmic protein in recombinant E. coli. Biotechnology Letters ,13, 311-316 (1991). DOI
- Tsolis, K.C., Hamed, M.B., Simoens, K., Koepff, J., Busche, T., Rückert, C., Oldiges, M., Kalinowski, J., Anné, J., Kormanec, J., Bernaerts, K., Karamanou, S., Economou, A. (2019) Secretome dynamics in a gram-positive bacterial model. Molecular & cellular proteomics, 18(3), 423-436. DOI
- Gwynne, D., Buxton, F., Williams, S., Garven S., Wayne Davies R. (1987) Genetically engineered secretion of active human interferon and a bacterial endoglucanase from Aspergillus Nidulans. Nature biotechnology, 5, 713-719. DOI
- Freitas, M., Souza, P., Homem-de-Mello, M., Fonseca-Bazzo, Y.M., Silveira, D., Ferreira Filho E.X., Pessoa Junior, A., Sarker, D., Timson, D., Inácio, J., Magalhães, P.O. (2022) L-asparaginase from Penicillium sizovae produced by a recombinant Komagataella phaffii strain. Pharmaceuticals, 15(6), 746-763. DOI
- Schwarzhans, J. P., Luttermann, T., Geier, M., Kalinowski, J., Friehs, K. (2017). Towards systems metabolic engineering in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology advances, 35(6), 681-710. DOI
- Hitzeman, R.A., Leung, D.W., Perry, L.J., Kohr, W.J., Levine, H.L., Goeddel, D.V. (1983) Secretion of human interferons by yeast. Science, 219(4585), 620-625. DOI
- Yang, Z., Zhang, Z. (2018) Engineering strategies for enhanced production of protein and bio-products in Pichia pastoris: A review. Biotechnology advances, 36(1), 182-195. DOI
- Biasoto, H.P., Hebeda, C.B., Farsky, S.H.P., Pessoa, A., Costa-Silva, T.A., Monteiro, G. (2023) Extracellular expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae’s L-asparaginase II in Pichia pastoris results in novel enzyme with better parameters. Preparative biochemistry & biotechnology, 53(5), 511-522. DOI
- Feng, Y., Liu, S., Jiao, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, M., Du, G. (2019) Gene cloning and expression of the L-asparaginase from Bacillus cereus BDRD-ST26 in Bacillus subtilis WB600. Journal of bioscience and bioengineering, 127(4), 418- 424. DOI
- Kim, S.K., Min, W.K., Park, Y.C., Seo, J.H. (2015) Application of repeated aspartate tags to improving extracellular production of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase isozyme II. Enzyme and microbial technology, 79-80, 49-54. DOI
- Caetano, L. F. (2020). Production and characterization of mutants of lower immunogenic potential of L-asparaginase II from Escherichia coli: Combination of in silico and in vitro studies, in postgraduate program in pharmacology. Universidade Federal Do Ceará: Available at: https://repositorio. ufc.br/handle/riufc/55993
- Butt, T.R., Jonnalagadda, S., Monia, B.P., Sternberg, E.J., Marsh, J.A., Stadel, J.M., Ecker, D.J., Crooke, S.T. ( 1989) Ubiquitin fusion augments the yield of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America, 86(8), 2540-2544. DOI
- Baker, R.T., Smith, S.A., Marano, R., McKee, J., Board, P.G. (1994) Protein expression using cotranslational fusion and cleavage of ubiquitin. Mutagenesis of the glutathione-binding site of human Pi class glutathione S-transferase.The Journal of biological chemistry, 269(41), 25381-25386. DOI
- Paraskevopoulou, V., Falcone, F.H. (2018) Polyionic tags as enhancers of protein solubility in recombinant potein expression. Microorganisms, 6(2), 47. DOI
- LaVallie, E.R., McCoy, J.M. (1995) Gene fusion expression systems in Escherichia coli. Current opinion in biotechnology, 6(5), 501-506. DOI
- Uhlén, M., Forsberg, G., Moks, T., Hartmanis, M., Nilsson, B. (1992) Fusion proteins in biotechnology. Current opinion in biotechnology, 3(4), 363- 369. DOI
- Wall, J.G., Plückthun, A. (1995) Effects of overexpressing folding modulators on the in vivo folding of heterologous proteins in Escherichia coli. Current opinion in biotechnology, 6(5), 507-516. DOI
- LaVallie, E.R., DiBlasio, E.A., Kovacic, S., Grant, K.L., Schendel, P.F., McCoy, J.M. (1993) A thioredoxin gene fusion expression system that circumvents inclusion body formation in the E. coli cytoplasm. Biotechnology (N Y), 11(2), 187-193. DOI
- Van Trimpont, M., Schalk, A.M., De Visser, Y., Nguyen, H.A., Reunes, L., Vandemeulebroecke, K., Peeters, E., Su, Y., Lee, H., Lorenzi, P.L., Chan, W.K., Mondelaers, V., De Moerloose, B., Lammens, T., Goossens, S., Van Vlierberghe, P., Lavie, A. (2023) In vivo stabilization of a less toxic asparaginase variant leads to a durable antitumor response in acute leukemia. Haematologica, 108(2), 409-419. DOI
- Ryu, J., Yang, S.J., Son, B., Lee, H., Lee, J., Joo, J., Park, H.H., Park, T.H. (2022) Enhanced anti-cancer effect using MMP-responsive L-asparaginase fused with cell-penetrating 30Kc19 protein. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology, 50(1), 278-285. DOI
- Guo, L., Wang, J., Qian, S., Yan, X., Chen, R., Meng, G. (2000) Construction and structural modeling of a single-chain Fv-asparaginase fusion protein resistant to proteolysis. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 70(4), 456-463. DOI
- Butt, T.R., Edavettal, S.C., Hall, J.P., Mattern, M.R. (2005) SUMO fusion technology for difficult-to-express proteins. Protein expression and purification, 43(1), 1-9. DOI
- Komolov А., Sannikova, E., Gorbunov, A., Gubaidullin, I., Plokhikh, K., Konstantinova, G., Bulushova, N., Kuchin, S., Kozlov, D. (2023) Synthesis of biologically active proteins as L6KD‐SUMO fusions forming inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and Bioengineering.121(2), 535-550. DOI
- Harper, S., Speicher, D.W. (2011) Purification of proteins fused to glutathione S-transferase. Methods in molecular biology, 681, 259-280. DOI
- Dieterich, D.C., Landwehr, M., Reissner, C., Smalla, K.H., Richter, K., Wolf, G., Böckers, T.M., Gundelfinger, E.D., Kreutz, M.R. (2003) Gliap--a novel untypical L-asparaginase localized to rat brain astrocytes. Journal of neurochemistry, 85(5), 1117-1125. DOI
- Costa, S.J., Almeida, A., Castro, A., Domingues, L., Besir, H. (2013) The novel Fh8 and H fusion partners for soluble protein expression in Escherichia coli: a comparison with the traditional gene fusion technology. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 97(15), 6779-6791. DOI
- Naderi, M., Ghaderi, R., Khezri, J., Karkhane, A., Bambai, B. (2022) Crucial role of non-hydrophobic residues in H-region signal peptide on secretory production of L-asparaginase II in Escherichia coli. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 636, 105-111. DOI
- Buchner, J. (1996) Supervising the fold: functional principles of molecular chaperones. FASEB journal : official publication of the federation of american societies for experimental biology, 10(1), 10-19. DOI
- Clarke, A.R. (1996) Molecular chaperones in protein folding and translocation. Current opinion in structural biology, 6(1), 43-50. DOI
- Ellis, R.J., Hartl, F.U. (1996) Protein folding in the cell: competing models of chaperonin function. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of american societies for experimental biology, 10(1), 20-26. DOI
- Gilbert, H.F. (1994) Protein chaperones and protein folding. Current opinion in biotechnology, 5(5), 534-539. DOI
- Martin, J., Hartl, F.U. (1994) Molecular chaperones in cellular protein folding. BioEssays : news and reviews in molecular, cellular and developmental biology, 16(9), 689-692. DOI
- Balchin, D., Hayer-Hartl, M., Hartl, F.U. (2020) Recent advances in understanding catalysis of protein folding by molecular chaperones. FEBS letters, 594(17), 2770-2781. DOI
- Fatima, K., Naqvi, F., Younas, H. ( 2021) A Review: Molecular Chaperonemediated folding, unfolding and disaggregation of expressed recombinant proteins. Cell biochemistry and biophysics, 79(2), 153-174. DOI
- Goloubinoff, P., Gatenby, A.A., Lorimer, G.H. (1989) GroE heat-shock proteins promote assembly of foreign prokaryotic ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oligomers in Escherichia coli. Nature, 337(6202), 44-47. DOI
- Hockney, R.C. (1994) Recent developments in heterologous protein production in Escherichia coli. Trends in biotechnology, 12(11), 456-463. DOI
- Lee, S.C., Olins, P.O. (1992) Effect of overproduction of heat shock chaperones GroESL and DnaK on human procollagenase production in Escherichia coli. The Journal of biological chemistry, 267(5), 2849-2852. DOI
- Goliloo, E. B., Tollabi, M., Jaliani, H. Z. (2021) Soluble expression and purification of Q59L mutant L-asparaginase in the presence of chaperones in SHuffle™ T7 strain. International journal of medical laboratory, 8(2), 6278. DOI
- Lobstein, J., Emrich, C.A., Jeans, C., Faulkner, M., Riggs, P., Berkmen, M. (2012) SHuffle, a novel Escherichia coli protein expression strain capable of correctly folding disulfide bonded proteins in its cytoplasm. Microb Cell Fact 11, 753. DOI
- Utami, D.F., Azizah, M.I., Sriwidodo, S., Haryanto, R.A., Pratiwi, R.D., Maksum, I. (2023) Review Article: Effect of co-expression chaperones on the expression of intracellular recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Chimica et natura acta, 11(2), 25-33. 10.24198/cna.v11.n2.46480
- Caspers, P., Stieger, M., Burn, P. (1994) Overproduction of bacterial chaperones improves the solubility of recombinant protein tyrosine kinases in Escherichia coli. Cellular and molecular biology (Noisy-le-grand), 40(5), 635-644.
- Blum, P., Ory, J., Bauernfeind, J., Krska, J. (1992) Physiological consequences of DnaK and DnaJ overproduction in Escherichia coli. Journal of bacteriology, 174(22), 7436-7444. DOI
- Sato, K., Sato, M.H., Yamaguchi, A., Yoshida, M. (1994) Tetracycline/ H+ antiporter was degraded rapidly in Escherichia coli cells when truncated at last transmembrane helix and this degradation was protected by overproduced GroEL/ES. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 202(1), 258-264. DOI
- Langer, T., Lu, C., Echols, H., Flanagan, J., Hayer, M.K., Hartl, F.U. (1992) Successive action of DnaK, DnaJ and GroEL along the pathway of chaperone-mediated protein folding. Nature, 356(6371), 683-689. DOI
- Seyed Hosseini, Fin. N.A., Barshan-Tashnizi, M., Sajjadi, S.M., Asgari, S., Mohajerani, N., Mirzahoseini, H. (2019) The effects of overexpression of cytoplasmic chaperones on secretory production of hirudin-PA in E. coli. Protein expression and purification, 157, 42-49. DOI
- Humphreys, D.P., Weir, N., Mountain, A., Lund, P.A. (1995) Human protein disulfide isomerase functionally complements a dsbA mutation and enhances the yield of pectate lyase C in Escherichia coli. The Journal of biological chemistry, 270(47), 28210-28215. DOI
- Ostermeier, M., De Sutter, K., Georgiou, G. (1996) Eukaryotic protein disulfide isomerase complements Escherichia coli dsbA mutants and increases the yield of a heterologous secreted protein with disulfide bonds. The Journal of biological chemistry, 271(18), 10616-10622. DOI
- Cole, P.A. (1996) Chaperone-assisted protein expression. Structure, 4(3), 239-242. DOI
- Yasukawa, T., Kanei-Ishii, C., Maekawa, T., Fujimoto, J., Yamamoto, T., Ishii, S. (1995) Increase of solubility of foreign proteins in Escherichia coli by coproduction of the bacterial thioredoxin. The Journal of biological chemistry, 270(43), 25328-25331. DOI
- Jena, R., Garg, D.K., Choudhury, L., Saini, A., Kundu, B. (2018) Heterologous expression of an engineered protein domain acts as chaperone and enhances thermotolerance of Escherichia coli. International journal of biological macromolecules, 107(Pt B), 2086-2093. DOI
- Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Lv, X., Fan, J., Zhang, J., Sun, J., Shen, Y. (2018) GroEL/ES mediated the in vivo recovery of TRAIL inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli. Scientific reports, 8(1), 15766. DOI
- Rudolph, R., Lilie, H. (1996) In vitro folding of inclusion body proteins. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 10(1), 49-56. DOI
- Schein, C.H. (1991) Optimizing protein folding to the native state in bacteria. Current opinion in biotechnology, 2(5), 746-750. DOI
- Schein, C.H. (1993) Solubility and secretability. Current opinion in biotechnology, 4(4), 456-461. DOI
- Ki, M.R., Pack, S.P. (2020) Fusion tags to enhance heterologous protein expression. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 104(6), 2411-2425. DOI
- Proba, K., Ge, L., Plückthun, A. (1995) Functional antibody single-chain fragments from the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli: influence of thioredoxin reductase (TrxB). Gene, 159(2), 203-207. DOI
- Sørensen, H.P., Mortensen, K.K. (2005) Soluble expression of recombinant proteins in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Microbial Cell Factories, 4(1), 1. DOI
- Dale, G.E., Broger, C., Langen, H., D’Arcy, A., Stüber, D. (1994) Improving protein solubility through rationally designed amino acid replacements: solubilization of the trimethoprim-resistant type S1 dihydrofolate reductase. Protein engineering, 7(7), 933-939. DOI
- Rinas, U., Tsai, L.B., Lyons, D., Fox, G.M., Stearns, G., Fieschko, J., Fenton, D., Bailey, J.E. (1992) Cysteine to serine substitutions in basic fibroblast growth factor: effect on inclusion body formation and proteolytic susceptibility during in vitro refolding. Biotechnology (N Y), 10(4), 435-440. DOI
- Amrein, K.E., Takacs, B., Stieger, M., Molnos, J., Flint, N.A., Burn, P. (1995) Purification and characterization of recombinant human p50csk proteintyrosine kinase from an Escherichia coli expression system overproducing the bacterial chaperones GroES and GroEL. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92(4), 1048-1052. DOI
- Cabilly, S. (1989) Growth at sub-optimal temperatures allows the production of functional, antigen-binding Fab fragments in Escherichia coli. Gene, 85(2), 553-557. DOI
- Shirano, Y., Shibata, D. (1990) Low temperature cultivation of Escherichia coli carrying a rice lipoxygenase L-2 cDNA produces a soluble and active enzyme at a high level. FEBS letters, 271(1-2), 128-130. DOI
- Blackwell, J.R., Horgan, R. (1991) A novel strategy for production of a highly expressed recombinant protein in an active form. FEBS letters, 295(1-3), 10-12. DOI
- Bowden, G. A., Georgiou, G. (1988). The effect of sugars on β‐lactamase aggregation in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology progress, 4(2), 97-101. DOI
- Sugimoto, S., Yokoo, Y., Hatakeyama, N., Yotsuji, A., Teshiba, S., Hagino. H. (1991) Higher culture pH is preferable for inclusion body formation of recombinant salmon growth hormone in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology Letters, 13, 385-388. DOI
- Umetsu, M., Tsumoto, K., Ashish, K., Nitta, S., Tanaka, Y., Adschiri, T., Kumagai, I. (2004) Structural characteristics and refolding of in vivo aggregated hyperthermophilic archaeon proteins. FEBS letters, 557(1-3), 49-56. DOI
- Ventura, S., Villaverde, A. (2006). Protein quality in bacterila inclusion bodies. Trends in biotechnology, 24(4), 179-185. DOI
- Peternel, S., Komel, R. (2010). Isolation of biologically active nanomaterial (inclusion bodies) from bacterial cells. Microbial Cell Factories, 9(1), 66. DOI
- Peternel, S., Komel, R. (2011) Active protein aggregates produced in Escherichia coli. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(11), 8275- 8287. DOI
- Vallejo, L.F., Rinas, U. (2004) Strategies for the recovery of active proteins through refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. Microbial Cell Factories, 3(1), 11. DOI
- Kante, R.K., Vemula, S., Somavarapu, S., Mallu, M.R., Boje Gowd, B.H., Ronda. S.R. (2018) Optimized upstream and downstream process conditions for the improved production of recombinant human asparaginase (rhASP) from Escherichia coli and its characterization. Biologicals, 56, 45-53. DOI
- Singhvi, P., Verma, J., Panwar, N., Wani, T.Q., Singh, A., Qudratullah, M., Chakraborty, A., Saneja, A., Sarkar, D.P., Panda, A.K. (2021) Molecular attributes associated with refolding of inclusion body proteins using the freezethaw method. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 618559. DOI
- Rajendran, V., Pushpavanam, S., Jayaraman, G. (2022) Continuous refolding of L-asparaginase inclusion bodies using periodic counter-current chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A., 1662(901), 462746. DOI
- Clark, E.D. (2001) Protein refolding for industrial processes. Current opinion in biotechnology, 12(2), 202-207. DOI
- Singh, A., Upadhyay, V., Upadhyay, A.K., Singh, S.M., Panda, A.K. (2015) Protein recovery from inclusion bodies of Escherichia coli using mild solubilization process. Microbial Cell Factories, 14(1), 41. DOI
- Singh, A., Upadhyay, V., Singh, A., Panda, A.K. (2022) Structurefunction relationship of inclusion bodies of a multimeric protein. Frontiers of Microbiology. 8(11),876. DOI
- Yuan, T. Z., Ormonde, C., Kudlacek, S.T., Kunche, S., Smith, J.N., Brown, W.A., Pugliese, K.M., Olsen, T., Iftikhar, M., Raston, C., Weiss, G.A. (2015). Shear-stress-mediated refolding of proteins from aggregates and inclusion bodies. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 16 (3), 393- 396. DOI
- Mukhopadhyay, A. (1997) Inclusion bodies and purification of proteins in biologically active forms. Advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology, 56, 61-109. DOI
- Burgess, R.R. (2009) Refolding solubilized inclusion body proteins. Methods in enzymology, 463, 259-282. DOI
- Ford, C.F., Suominen, I., Glatz, C.E. (1991) Fusion tails for the recovery and purification of recombinant proteins. Protein expression and purification, 2(2-3), 95-107. DOI
- Yamanè, T., Shimizu, S. (2006). Fed-batch techniques in microbial processes. Advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology, 30, 147-194. DOI
- Baeshen, M. N., Al-Hejin, A. M., Bora, R. S., Ahmed, M. M., Ramadan, H. A., Saini, K. S., Baeshen, N. A., Redwan, E. M. (2015). Production of biopharmaceuticals in E. coli: Current scenario and future perspectives. Journal of microbiology and biotechnology, 25(7), 953-962. DOI
- Yee, L, Blanch, H.W. (1992) Recombinant protein expression in high cell density fed-batch cultures of Escherichia coli. Biotechnology (N Y), 10(12), 1550-1556. DOI
- Doriya, K., Jose, N., Gowda, M., Kumar, D.S. (2016) Solid-state fermentation vs submerged fermentation for the production of L-asparaginase. Advances in food and nutrition research, 78:115-135. DOI
- Luli, G.W., Strohl, W.R. (1990) Comparison of growth, acetate production, and acetate inhibition of Escherichia coli strains in batch and fed-batch fermentations. Applied and environmental microbiology, 56(4), 1004-1011. DOI
- Aristidou, A.A., San, K.Y., Bennett, G.N. (1995) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to enhance recombinant protein production through acetate reduction. Biotechnology progress, 11(4), 475-478. DOI
- San, K.Y., Bennett, G.N., Aristidou, A.A., Chou, C.H. (1994) Strategies in high-level expression of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli. Annals of the New York academy of sciences, 721, 257-267. DOI
- Jacques, N., Guillerez, J., Dreyfus, M. (1992) Culture conditions differentially affect the translation of individual Escherichia coli mRNAs. Journal of molecular biology, 226(3), 597-608. DOI
- Hymavathi, M., Sathish, T., Subba Rao, Ch., Prakasham. R.S. (2009) Enhancement of L-asparaginase production by isolated Bacillus circulans (MTCC 8574) using response surface methodology. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 159(1), 191-198. DOI
- Mihooliya, K.N., Nandal. J., Kumari, A., Nanda, S., Verma, H., Sahoo, D.K. (2020) Studies on efficient production of a novel L-asparaginase by a newly isolated Pseudomonas resinovorans IGS-131 and its heterologous expression in Escherichia coli. 3 Biotechnology, 10(4), 148. DOI
- Kwon, S., Kim, S., Kim, E. (1996) Effects of glycerol of beta-lactamase production during high cell density cultivation of recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnology progress, 12(2), 205-208. DOI
- Barros, T., Brumano, L., Freitas, M., Pessoa, A., Junior, Parachin, N., Magalhães, P.O. (2020) Development of processes for recombinant L-asparaginase II production by Escherichia coli Bl21 (De3): from shaker to bioreactors. Pharmaceutics, 13(1), 14. DOI
- Ghoshoon, M.B., Berenjian, A., Hemmati, S., Dabbagh, F., Karimi, Z., Negahdaripour, M., Ghasemi, Y. (2015) Extracellular production of recombinant L-asparaginase II in Escherichia coli: medium optimization using response surface methodology. International journal of peptide research and therapeutics, 21(4), 487-495. DOI
- Ukkonen, K., Neubauer, A., Pereira, V.J., Vasala, A. (2017) High yield of recombinant protein in shaken E. coli cultures with enzymatic glucose release medium En Presso B. In heterologous gene expression in E.coli. Methods in molecular biology (Burgess-Brown, N. eds), Humana Press, New York, NY. 1586, 127-137. DOI
- Moorthy, V., Ramalingam, A., Alagarsamy, S., Shankaranaya, R. (2010) Production, purification and characterisation of extracellular L-asparaginase from a soil isolate of Bacillus sp. African journal of microbiology research bengaluru, 4(560), 1862-1867, http://www.academicjournals.org/ajmr
- Thirunavukkarasu N., Suryanarayanan N.S., Murali T.S., Ravishankar J.A.P., Gummadi, S. (2011) L-asparaginase from marine derived fungal endophytes of seaweeds. Mycosphere. 2(2), 147-155.
- Ariga, O., Andoh,Y., Fujishita,Y., Watari, T., Sano, Y. (1991) Production of thermophilic a-amylase using immobilized transformed Escherichia coli by addition of glycine. Journal of fermentation and bioengineering, 71(6), 397-402. DOI
- Ghosh, S., Murthy, S., Govindasamy, S., Chandrasekaran, M. (2013) Optimization of L-asparaginase production by Serratia marcescens (NCIM 2919) under solid state fermentation using coconut oil cake. Sustainable chemical processes, 1(1), 9. DOI
- Trang, T.H.N., Cuong, T.N., Thanh, S.L.N., Tuyen, T. D. (2016) Optimization, puriication and characterization of recombinant L-asparaginase II in Escherichia coli. African journal of biotechnology, 15(31), 1681-1691. DOI
- Borah, D., Yadav, R., Sangra, A., Shahin, L., Anand, A., Chaubey, K. (2012) Production, purification and process optimization of asparaginases (an anticancer enzyme) from E. coli, from sewage water. International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences. 4(4), 560-563.
- Muharram, M., Abulhamd A., Salem-Bekhet, M. (2014) Recombinant expression, purification of L-asparaginase-II from thermotolerant E. Coli strain and evaluation of its antiproliferative activity. African journal of microbiology research, 8(15), 1610-1619. DOI
- Vidya, J., Vasudevan, U.M., Soccol, C., Pandey, A. (2011) Cloning,functional expression and characterization of L-asparaginase II from E. coli MTCC 739. Food technology and biotechnology. 49(3), 286-290. https:// hrcak.srce.hr/71053. Accessed 27 May 2024
- Baskar, G., Rajasekar,V.,Renganathan, S. (2011) Modeling and Optimization of L-asparaginase Production by Enterobacter Aerogenes Using Artificial Neural Network Linked Genetic Algorithm. International Journal of Chemical Engineering and Applications, 2(2), 98-100. DOI
- Goswami, R., Veeranki, V.D., Mishra, V.K. (2019) Optimization of process conditions and evaluation of pH & thermal stability of recombinant L-asparaginase II of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica SCRI 1043 in E. coli. Biocatalysis and agricultural biotechnology, 22(3), 101377. DOI
- Ebrahimi,V., Hashemi, A.( 2024) Optimizing recombinant production of L-asparaginase 1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae using response surface methodology. Folia Microbiologica 69(6),1-15. DOI
- Çalık, P., Ata, O., Güneş, H., Massahi, A., Boy, E., Keskin, A., Oztürk, S., Zerze, G.H., Ozdamar, T.H. (2015) Recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris under glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter:from carbon source metabolism to bioreactor operation parameters. Biochemical engineering journal, 95, 20-36. DOI
- Looser, V., Bruhlmann, B., Bumbak, F., Stenger, C., Costa, M., Camattari, A., Fotiadis, D., Kovar, K. (2015) Cultivation strategies to enhance productivity of Pichia pastoris: A review. Biotechnology advances, 33(6 Pt 2), 1177-1193. DOI
- Abribat, T. (2023) Pegylated L-asparaginase. United States: Carpmaels, Ransford LLP. Patent No. EP10730170.7
- Trieu, V. (2010). Albumin binding peptide-mediated disease targeting. CA: Ridout and Maybee LLP. Patent No. 2867252
- Lavie, A., Nguyen, H. (2017) L-asparaginase variants and FUSION proteins with reduced L-glutaminase activity and enhanced stability. WO. Patent No. US2017/020090
- Chahardahcherik, M., Ashrafi, M., Ghasemi, Y., Aminlari, M. (2020) Effect of chemical modification with carboxymethyl dextran on kinetic and structural properties of L-asparaginase. Analytical biochemistry, 591(6), 113537. DOI
- Qian, G., Zhou, J., Ma, J., Wang, D., He, B. (1996) The chemical modification of E. coli L-asparaginase by N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan. Artificial cells, blood substitutes, and immobilization biotechnology, 24(6), 567-577. DOI
- Sindhu, R., Pradeep, H., Manonmani, H.K. (2019) Polyethylene glycol acts as a mechanistic stabilizer of L-asparaginase: A computational probing. Medicinal chemistry (Shariqah (United Arab Emirates)), 15(6), 705-714. DOI
- Cerofolini, L., Giuntini, S., Carlon, A., Ravera, E., Calderone, V., Fragai, M., Parigi, G., Luchinat, C. (2019) Characterization of PEGylated asparaginase: new opportunities from NMR analysis of large PEGylated therapeutics. Chemistry, 25(8), 1984-1991. DOI
- Veronese, F.M., Pasut, G. (2005) PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug discovery today,10(21), 1451-1458. DOI
- MacDonald, T., Kulkarni, K., Bernstein, M., Fernandez, C.V. (2016) Allergic reactions with intravenous compared with intramuscular pegaspargase in children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study from the maritimes, Canada. Journal of pediatric hematology/oncology, 38(5), 341-344. DOI
- Dobryakova, N.D., Kudryashova, E.V. (2023) Stabilization of Erwinia carotovora and Rhodospirillum rubrum L-asparaginases in complexes with polycations. Applied biochemistry and microbiology, 59(9), 1183-1191. DOI